What is the perfect square trinomial for \((x + 5)^2\)?
\(x^2 + 10x + 25\)
\(x^2 + 15x + 25\)
\(x^2 + 10x + 20\)
\(x^2 + 25x + 25\)

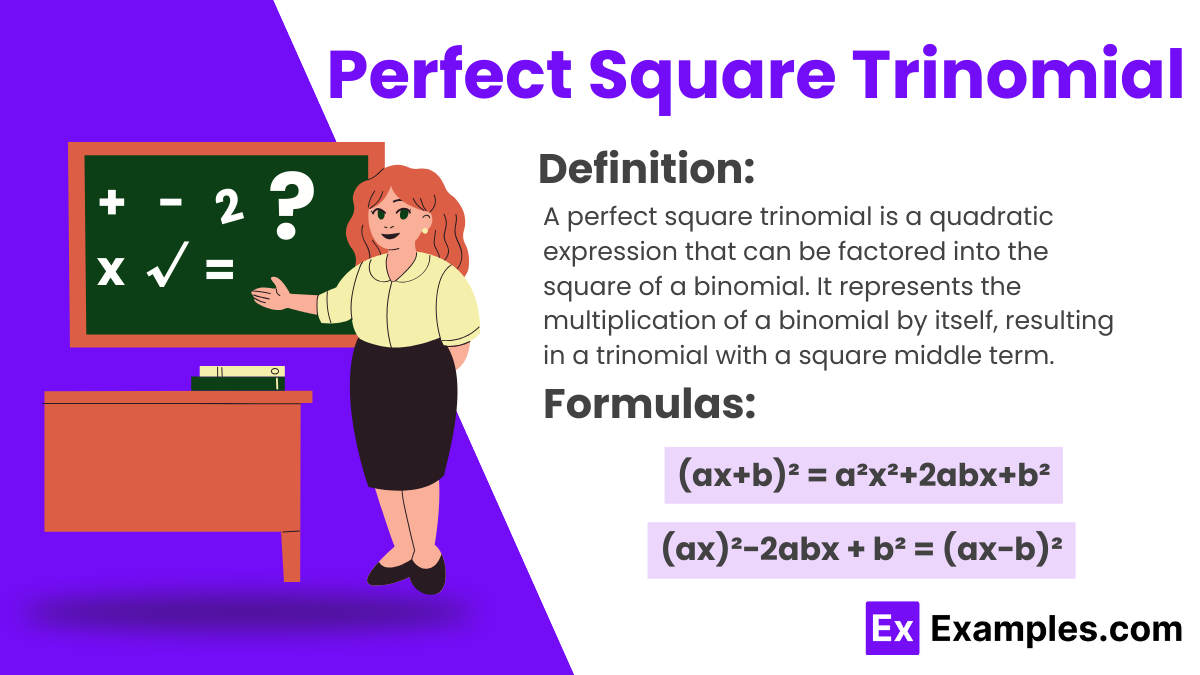
Exploring Perfect Square Trinomials unveils essential principles of algebra, encompassing rational and irrational numbers, squares, and square roots. These trinomials represent quadratic expressions that can be factored into identical binomial factors, showcasing the symmetry and structure inherent in quadratic equations. Understanding Perfect Square Trinomials is crucial in algebraic manipulation, number theory, and statistical analysis, providing insights into least square methods and polynomial functions. Mastery of these trinomials enhances proficiency in mathematical reasoning and problem-solving across various domains.
The formulas for a Perfect Square Trinomial is:
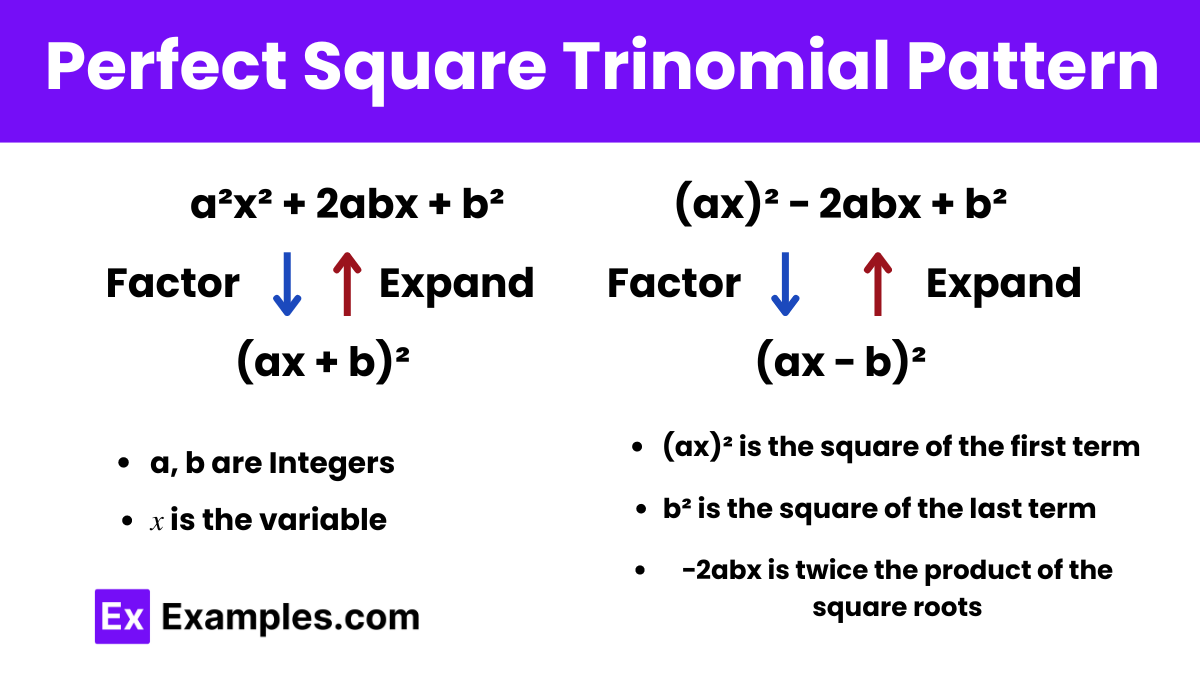
(ax)²−2abx + b² = (ax−b)²
Where 𝑎 and 𝑏 are integers, s of the quadratic expression, and 𝑥 is the variable. This formula represents the expansion of a squared binomial, showcasing the symmetrical structure of the trinomial and its relationship to the original expression. It is a fundamental tool in algebraic manipulation, factorization, and solving quadratic equations.
Perfect Square Trinomials are used in various mathematical applications, including geometry, physics, and engineering. They are employed in solving problems involving areas, volumes, distances, and optimization.
erfect Square Trinomials are a type of quadratic expression, not necessarily a quadratic equation, as they represent a specific form of quadratic polynomial that can be factored into the square of a binomial. They are a tool for solving quadratic equations and understanding quadratic functions but are distinct from equations, which involve expressions set equal to one another.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the perfect square trinomial for \((x + 5)^2\)?
\(x^2 + 10x + 25\)
\(x^2 + 15x + 25\)
\(x^2 + 10x + 20\)
\(x^2 + 25x + 25\)
Which of the following is a perfect square trinomial?
\(x^2 - 5x + 8\)
\(x^2 - 6x + 9\)
\(x^2 + 4x + 7\)
\(x^2 - 8x + 10\)
Identify the correct factorization of \(x^2 + 12x + 36\).
\((x + 18)^2\)
\((x - 6)^2\)
\((x + 6)^2\)
\((x - 18)^2\)
Which expression represents a perfect square trinomial?
\(x^2 + 8x + 16\)
\(x^2 + 9x + 20\)
\(x^2 - 10x + 30\)
\(x^2 - 4x + 5\)
What is the expansion of \((x - 7)^2\)?
\(x^2 + 14x + 49\)
\(x^2 - 49x + 49\)
\(x^2 + 49x + 49\)
\(x^2 - 14x + 49\)
Which of the following is not a perfect square trinomial?
\(x^2 + 6x + 9\)
\(x^2 + 4x + 10\)
\(x^2 - 2x + 1\)
\(x^2 - 8x + 16\)
Find the perfect square trinomial of \((2x + 3)^2\).
\(4x^2 + 12x + 9\)
\(4x^2 + 6x + 9\)
\(4x^2 + 12x + 12\)
\(4x^2 + 9x + 9\)
Which trinomial is equivalent to \((x + 7)^2\)?
\(x^2 + 7x + 49\)
\(x^2 + 14x + 35\)
\(x^2 + 49x + 49\)
\(x^2 + 14x + 49\)
Identify the perfect square trinomial in the following:
\(4x^2 - 10x + 25\)
\(4x^2 - 20x + 25\)
\(4x^2 + 10x + 25\)
\(4x^2 - 20x + 20\)
Which expression represents \((3x - 4)^2\)?
\(9x^2 - 24x + 16\)
\(9x^2 - 8x + 16\)
\(9x^2 - 12x + 16\)
\(9x^2 + 24x + 16\)
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

