Interactive Period Table
Periodic Table for AP Chemistry to Practice
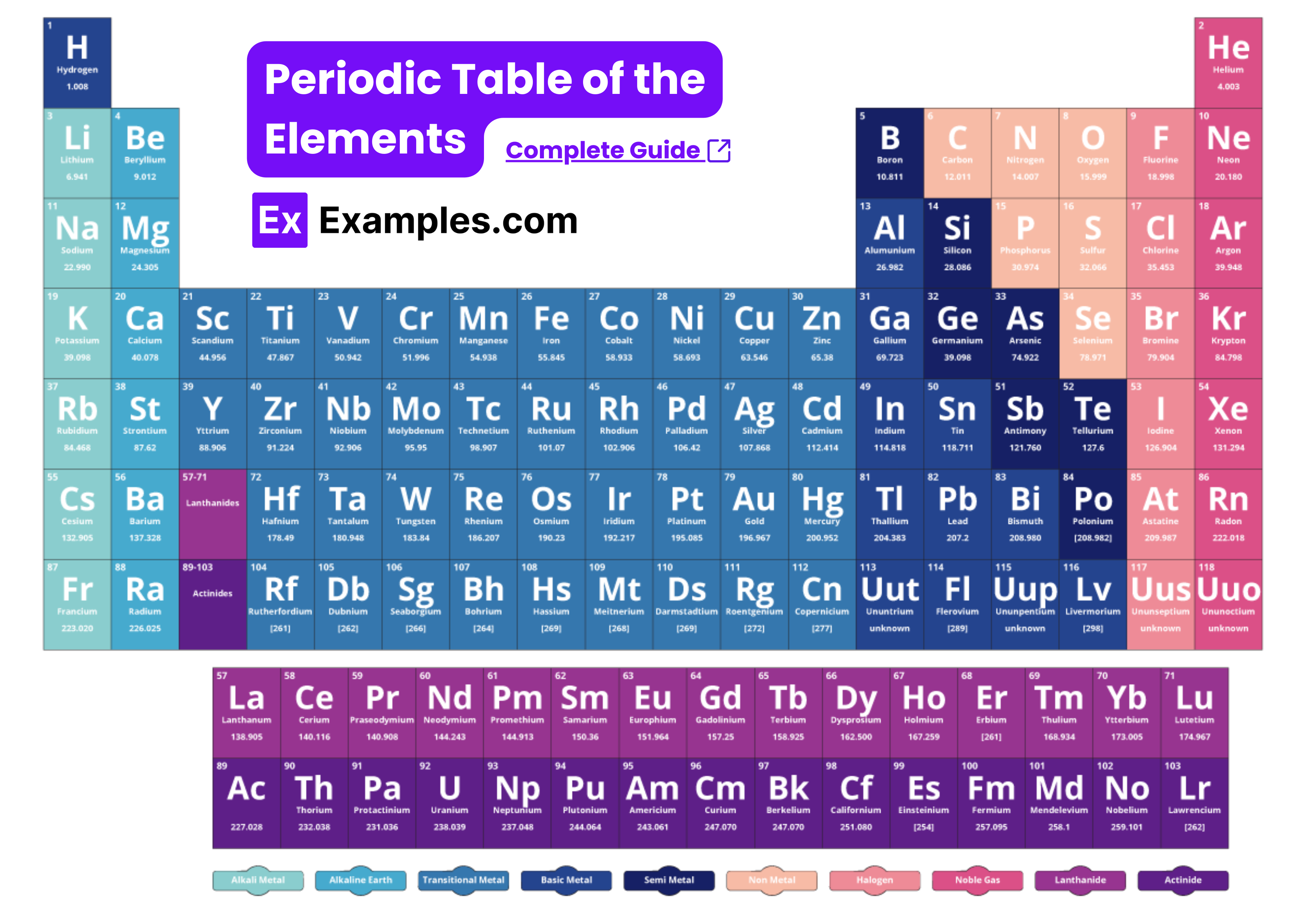
How to Use Periodic Table for AP Chemistry Success?
The periodic table is an essential tool for mastering AP Chemistry. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the provided AP Chemistry Periodic Table of the Elements to enhance your understanding and performance in the exam.
1. Understand the Layout
The periodic table is organized to provide a wealth of information at a glance:
- Groups (Columns): Elements in the same column have similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons.
- Periods (Rows): Elements in the same row have the same number of electron shells.
- Blocks: The table is divided into s, p, d, and f blocks based on the electron configuration.
2. Memorize Key Groups
Certain groups have specific properties that are frequently tested on the AP Chemistry exam:
- Group 1 (Alkali Metals): Highly reactive, especially with water.
- Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals): Reactive metals, though less so than alkali metals.
- Group 17 (Halogens): Very reactive nonmetals.
- Group 18 (Noble Gases): Inert gases, with very low reactivity.
3. Learn Periodic Trends
Understanding trends across periods and down groups is crucial:
- Atomic Radius: Decreases across a period, increases down a group.
- Ionization Energy: Increases across a period, decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: Increases across a period, decreases down a group.
4. Use Atomic Numbers and Symbols
Each element is identified by its atomic number (number of protons) and its symbol:
- Atomic Number: Helps determine the element’s position and properties.
- Element Symbol: A shorthand notation used in chemical equations and formulas.
5. Identify Element Groups and Periods
Knowing the position of an element can help predict its properties:
- Locate the Element: Find its group and period.
- Predict Properties: Use its position to infer reactivity, state of matter, and more.
6. Apply Electron Configuration
The table helps with writing electron configurations:
- Use the Blocks: s, p, d, and f blocks correspond to the filling of different orbitals.
- Determine Configuration: Starting from hydrogen, follow the order of filling orbitals.
7. Practice with Chemical Reactions
The periodic table helps predict the outcomes of chemical reactions:
- Reactivity Trends: Metals in groups 1 and 2 react vigorously with nonmetals in groups 16 and 17.
- Oxidation States: Transition metals can have multiple oxidation states, predictable by their position.
8. Utilize Color Coding and Other Annotations
Many periodic tables include color coding or other annotations:
- Metal vs. Nonmetal: Typically, metals are on the left and center, nonmetals on the right.
- State of Matter: Some tables indicate whether elements are solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature.
9. Memorize Essential Elements
For AP Chemistry, it’s helpful to memorize certain elements and their properties:
- Common Elements: Know the first 20 elements, their symbols, and basic properties.
- Transition Metals: Familiarize yourself with key transition metals and their common oxidation states.
10. Practice Problems
Regularly practicing problems will solidify your understanding of how to use the periodic table:
- Homework and Quizzes: Use the table to answer questions about trends, reactivity, and electron configurations.
- AP Practice Tests: Simulate test conditions and use the table as you would during the exam.
Tips & Tricks to Use Periodic Table in AP Chemistry Test
Using the periodic table effectively can significantly boost your performance in the AP Chemistry exam. Here are ten super tips and tricks to help you make the most of this essential tool:
1. Memorize Common Element Symbols and Atomic Numbers
- Why: Quickly identifying elements by their symbols and atomic numbers saves time during the exam.
- How: Flashcards or mnemonic devices can help with memorization.
2. Understand Periodic Trends
- Why: Trends like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity often come up in questions.
- How: Remember general rules: atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group, while ionization energy and electronegativity increase across a period and decrease down a group.
3. Use Group Properties
- Why: Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
- How: Know the properties of alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and noble gases to predict reactions and behavior.
4. Identify Block Elements
- Why: Understanding s, p, d, and f blocks helps with electron configurations and reactivity.
- How: Use the periodic table layout to determine which block an element belongs to and its electron configuration.
5. Leverage Oxidation States
- Why: Transition metals often have multiple oxidation states, which are crucial for redox reactions.
- How: Familiarize yourself with common oxidation states of transition metals and practice applying them in chemical equations.
6. Recognize Periodic Patterns
- Why: Patterns such as the diagonal relationship (e.g., Li and Mg) can help solve comparative questions.
- How: Study these patterns and understand their underlying principles to use them in problem-solving.
7. Practice Electron Configuration
- Why: Questions on electron configuration are common in the AP exam.
- How: Use the periodic table to write out electron configurations, remembering the order of orbital filling (s, p, d, f).
8. Use Color-Coding and Annotations
- Why: Some periodic tables are color-coded to indicate metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, which can quickly guide your responses.
- How: If your exam allows, annotate your periodic table during your study sessions to include key information like common oxidation states and trends.
9. Predict Reactivity and Bonding
- Why: The periodic table helps predict how elements will react and the types of bonds they will form.
- How: Understand that metals tend to lose electrons and form cations, while nonmetals tend to gain electrons and form anions.
10. Quick Reference for Calculations
- Why: You can use the periodic table to find atomic masses for stoichiometry calculations.
- How: Practice using the atomic masses in the periodic table for quick molar mass calculations during the exam.
Additional Tips for Exam Day:
- Highlight Key Sections: Before the exam, use a highlighter to mark important groups and periods, like the alkali metals and halogens.
- Draw Connections: Draw lines or arrows to indicate trends such as increasing ionization energy or electronegativity.
- Time Management: Use the periodic table to quickly check facts instead of trying to recall them from memory, saving valuable time.
Mastering the use of the periodic table is fundamental to success in AP Chemistry. By understanding its layout, memorizing key groups and trends, and practicing regularly, you will be well-prepared to tackle the exam. Use the provided periodic table as a constant reference throughout your studies. Happy studying!

