9+ Proposal to Buy a Business Examples to Download
When there is a business that you are interested in purchasing, the first step you’ll have to take is to write a proposal to buy a business letter. It is the most efficient medium you can use to express your interest and the general terms you would like to apply in the further negotiation of your offer.
The response that the other party will send to you regarding your offer will let you know if they are willing to sell the business to you. If they are, the rest of their formal letter will discuss what the next steps to be taken would be.
Proposal to Buy a Business Example

Business Proposal Example

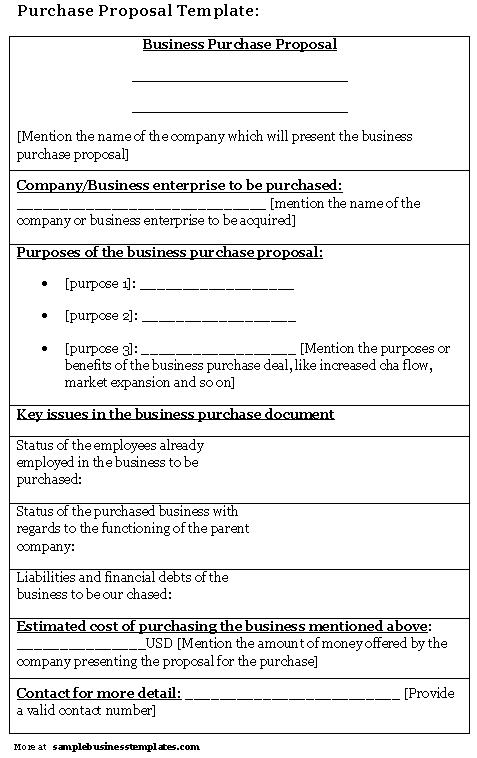
Business Proposal Template

Understanding Business Purchase Proposals
Your professional proposal will begin with a document known as a “term sheet.” The term sheet will serve as your offer letter that will detail the key terms of the transaction, such as the amount of money you are offering to pay for the business and its assets. It will also touch on how you are planning to treat the company’s debts and liabilities once the ownership is transferred to your name.
The term sheet will also discuss your decision regarding what will happen to the business’s current employees. Will there be jobs terminated, or will the people retain their current statuses?
However, despite these initial planning involved in the term sheet, the document will not serve as the seller and the buyer’s official contract. It will simply serve the role of a proposal that the seller will consider and review before deciding to accept or decline the buyer’s proposal to purchase the business. You may also see business proposal letter examples.
The business purchase proposal is simply one of the first steps you will have to take in the process of completing a sale. It will serve as a solid foundation for the transaction that may occur. The document will try to capture the interested buyer’s deal structure and terms. You may also like research proposal examples.
A general proposal is non-binding since it’s simply an offer made on paper and not a promise of anything absolute. However, there are two clauses to which both parties are bound such as the agreement to keep the offer confidential, and the commitment that the seller will refrain from discussing the sale with other interested buyers for a time period to allow the purchaser time to contact due diligence.
Since both parties are not bound by the simple proposal, they can back out of it for any reason at all. However, this is a very rare occurrence since most parties, at this point, have already spent a significant time negotiating, which means that they are closer to settling into a deal already.
The proposal to buy the business is the reference by which the attorneys of those involved can use to craft the final business sale agreement once the parties have decided to finalize the transaction. It will also provide a snapshot of how the deal will look like in the future since it discusses the terms that everyone must follow.
This is why it’s important that the proposal can already provide as much major detail as possible since there will really be no time left to negotiate once a general agreement has been made. Although there will be some sort of bargaining that will happen and some slight alterations to the original proposal, nothing so big that it will have a massive impact on the deal’s overall value.
Proposal to Buy a Business Sample Document
Proposal Letter of Intent to Acquire a Business Example
Due Diligence Checklist
Due diligence is the process of investigating the business or the person prior to signing a general contract as a standard of care. It may come as a legal obligation, but is more commonly a voluntary action.
A common example of due diligence in many industries is a potential acquirer’s evaluation of a target company and its assets that he wants to buy. This is conducted to result in a more informed decision-making that will help him make sounder judgement on the business’s costs, benefits, and risks. You may also see short proposal examples.
Although not a requirement, most businessmen choose to conduct a due diligence (preferably by their lawyers) to help them make sure that their purchase will be worth the money they will be putting into it.
Here is a short list of the most important due diligence checkup that you must conduct before purchasing a business:
1. Financial information about the company
- The last 3 years’ annual and quarterly financial information, including their balance sheets, cash flows, income statements, and footnotes
- The company’s planned projects versus their end results
- The management’s financial records
- Any existing customer backlog
- The next three years’ financial projections
- Major growth prospects and drivers
- Risks
2. Capital structure
- Existing outstanding shares
- List of stockholders
- Summary of all bank loans
- Liabilities
3. Other financial information
- Summary of current, federal, and any foreign tax positions
- General accounting policies, such as revenue
- Schedule of financing history for warrants, equity, and debt
4. Products
- Major applications and customers
- Projected and historical growth rates
- Market share analysis
- Analysis of the nature and speed of technological progress
- Product enhancements
- Cost structure analysis
5. Customer information
- A list of the past three year’s top fifteen customers and current year’s relevant contact information
- A list of strategic relationship
- Description of any important severed relationships within the last two years
- A list of the past three years’ top ten suppliers
- A description of the business’s competitive landscape
- The market position of the competition, its related strengths, and weaknesses
- The basis for the competition
You may also like project proposal examples.
6. Legal and related matters
- Any pending lawsuits against the company
- Any pending lawsuits initiated by the company
- Employee safety and environmental liability issues
- A list of trademarks, copyrights, licenses, and material-patents
- Summary of any material exposures or insurance coverage
- Summary of material contracts or other regulatory agency-related problem
You may also check out investment proposal examples.
Business Purchase Proposal Document
Proposal to Purchase Business Letter Example
Valuation
In your proposal, you will include the amount you are willing to pay in exchange for the business. If the amount is considerable, naturally, there’s a bigger chance that your simple proposal will be accepted by the seller. But, of course, you can’t just name a big number to offer for the property. You also have to make sure that you gain a profit from the purchase.
Valuation is the process of establishing the value of the business. By assessing how much the whole establishment is worth, minus its liabilities, you can come up with the amount you can pay for it.
One of the factors you can evaluate to get what a business is worth is by looking at their annual revenue. Another factor would be the company’s other outside investments. But if you can’t rely on yourself to be able to efficiently calculate these numbers, you can check with your accountant to have them review other similar businesses in your area to determine current valuation methods for the type of business that you are trying to acquire. You may also see freelance proposal examples.
Before deciding to purchase a business, make sure that you have obtained a complete list of the business’s equipment and inventory included in the sale. Also, include the value of the real estate, lease agreements, licenses, contracts, and clients in your estimation. You can hire an appraiser to help you place the value of these assets, and make sure you constantly review your accountant during the process.
It would also be smart to request audited finance and relevant simple income statements from the seller, including the detailed information on employee expenses and other outstanding liabilities such as credit accounts.
Once you have all these numbers and data in your possession, analyze the information with your accountant. You can then proceed to writing a purchase proposal based on the results of your general analysis. After that, you can even choose to start your letter with the most important detail: the purchase product.
Making an Offer
Once you have successfully conducted due diligence and valued the business, you can now proceed to making your negotiations, preferably with professional support and business advice. When you negotiate for the purchase of the business, you are bound to make an offer, which is usually followed by your seller’s counteroffer until you both bargain to reach a standard agreement.
Proposal to Purchase Asset
Negotiation Tips
During the negotiation, you must aim to make your offer tempting to the seller to make sure that you catch his attention. To successfully do that, here are a few tips you can follow:
1. Before setting out for the negotiation, make sure that you are already aware of your limit, or the highest price that you are prepared to pay for the business, and stick to it. You must remember that anything higher than that will no longer be a smart move. This is important for you to know that you actually left the negotiation acquiring more instead of leaving with less. You may also see budget proposal examples.
2. Never agree to the first price that the seller has quoted. Remember that this is only the starting point, most probably the maximum, and that he can go lower than that. He has only provided you with that amount only to give you an idea of the business’s price range. You are there to negotiate, after all. Don’t settle with the first digit. In business, the wisest man always gets more. Make sure that it’s you. You may also like conference proposal examples.
3. Open the negotiation with the lowest price you can give, although not so much that the seller will think that you are not serious about the purchase. If he doesn’t agree to that, at least you have a big allowance to work from.
4. Always take your time during negotiation. There’s no need to rush into bad decisions anyway. After all, this business might just be your main activity for the next few years, so make sure you’ve invested well. A few days or weeks worth of thinking and brainstorming can make the difference between purchasing the right business for you and not getting back your money’s worth. You may also check out business proposal cover letter examples.
5. Make your own list of items for the negotiation. As the buyer, the seller probably needs you as much as you need him, so grab the chance and make sure that he’s not the only one calling the shots here. Create separate categories of your list: what you can compromise on, and what you absolutely must have. You might be interested in security proposal examples.
6. Challenge your seller by asking “what if” questions such as “What if a major client goes bankrupt?” or “What if a key group of employees leave after the changeover?”
7. Do not show your seller that you are desperate to purchase the business (even if you are) and don’t reveal your real reasons for buying the business. He might use it to his advantage and make you pay more for the business or adjust to his conditions. Make sure you don’t get out of this transaction with a small profit. This is business, after all. You may also see fundraising proposal examples.
8. Avoid being overly critical toward the business and its seller. He is not a criminal under litigation, and you are not a judge. You are an interested buyer, which means that you’ve seen something in the business that makes you want to own it. Keep the conversation focused on facts. You may also like engineering project proposal examples.
9. Practice the negotiation beforehand, especially if this is your first time. Don’t go to that battle inexperienced.
10. Make sure that whatever outcome you will get from this transaction will satisfy you. Ideally, the result of the transaction should please both parties. (It’s called a negotiation for a reason.) But, if only one party is satisfied, make sure that it’s you. You may also check out software project proposal examples.
11. Be prepared to strike a deal if you’re comfortable with the price, and don’t hesitate to leave if you aren’t. There are still many, juicier fishes in the sea.
12. Keep your emotions away from the negotiations. (And this doesn’t have to be explained.) If you don’t think you can handle it yourself, ask a professional adviser to do it for you, or in behalf of you.
Bargaining
The seller’s interest will include wanting to make as much money as possible on the sale of the business. Of course, why would you sell something if you don’t want to make a profit out of it? Also, he will make sure than the sale transaction will be most advantageous for them, by avoiding contract conditions and liability ties they can’t (or don’t want) to meet. You may also see proposal memo examples.
You, on the other hand, are only interested in paying the least amount possible for the business, with the inclusion of as many tangible and intangible assets in the price. You also want to protect yourself from false claims from the seller and, most importantly, you want a bargain. You may also like policy proposal examples.
Proposal to Buy a Small Business Sample
Sample Proposal to Purchase Sample
By being smart with your negotiations, you just might successfully get out of this with more to gain. A shrewd bargainer would be able to do that. Make sure you are one.