What is the pH range of a basic solution?
0-3
3-7
7-10
7-14

Bases are substances that taste bitter and feel slippery when touched. In chemistry, they are known for turning red litmus paper blue and are commonly found in household items like baking soda and soap. Bases react with acids to form water and salts, a process called neutralization. When dissolved in water, bases release hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which contribute to their characteristic properties. This basic knowledge helps us understand how everyday substances interact and change, influencing everything from cooking to cleaning.
The term “base” in chemistry originates from the Latin word “basis,” meaning “foundation.” This term was first used in this context because bases are foundational to many chemical reactions, particularly those involving acids. In the early days of chemical research, scientists noted that certain substances had the consistent ability to neutralize acids and form water and salts. This ability to ‘base’ themselves against the effects of acids led to their classification as bases.
Bases are substances that can accept hydrogen ions (protons) or donate a pair of valence electrons to form a bond. This definition has evolved over time, stemming from the observation of their reactions with acids. The concept was further refined with the introduction of the Arrhenius definition, which identified bases as compounds that increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. This fundamental behavior in chemical reactions highlights their crucial role in forming the ‘base’ or foundation for further chemical transformations, thus justifying the name “base.”
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Taste | Bitter |
| Texture | Slippery |
| pH Level | Above 7 |
| Conductivity | Good conductors of electricity |
| Solubility | Varies (usually soluble in water) |
Bases have a distinctly bitter taste. This characteristic helps distinguish them from other substances, although tasting chemical substances is not recommended outside of controlled environments like food testing.
Bases feel slippery to the touch. This sensation occurs because bases react with the fatty acids on the skin, creating soap-like compounds that are smooth and slippery.
All bases have a pH greater than 7, placing them in the alkaline range. The pH scale is a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
Bases are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water. This is due to the release of ions, charged particles that facilitate the flow of electrical current.
The solubility of bases in water can vary. Strong bases like sodium hydroxide are highly soluble, while others, such as magnesium hydroxide, have lower solubility but still dissolve enough to be effective.
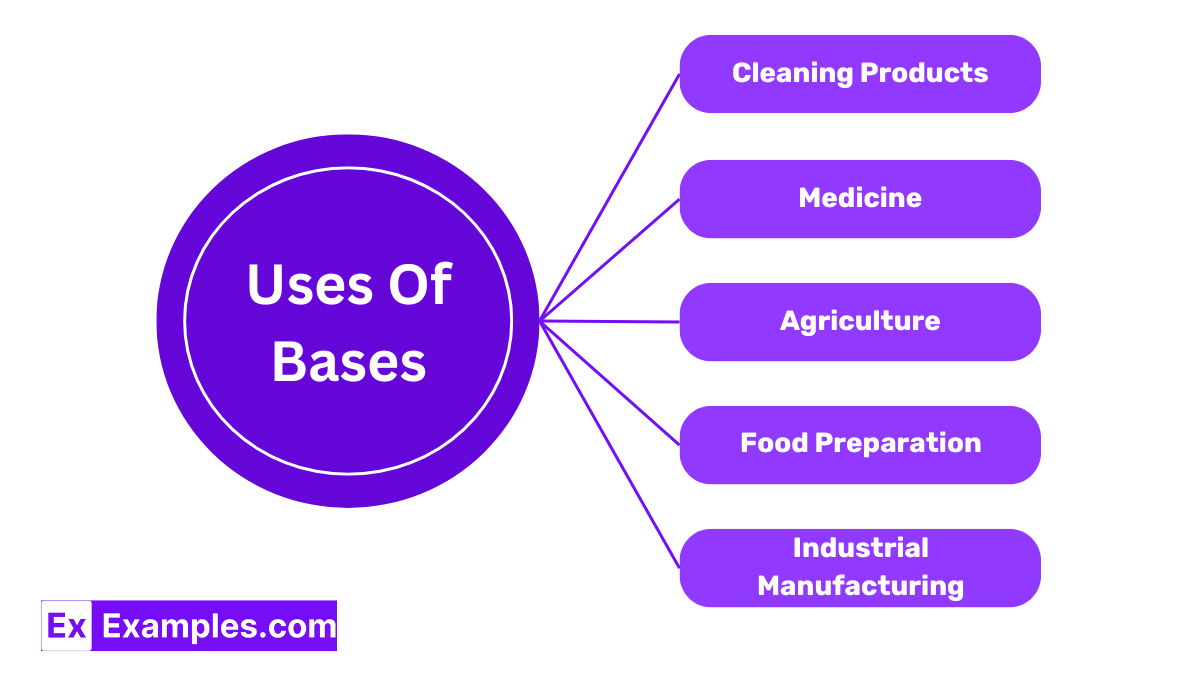
Many household cleaners contain bases such as ammonia. These cleaners are effective at removing grease and dirt because bases can react with fatty acids, breaking them down into soap-like substances that are easy to wash away.
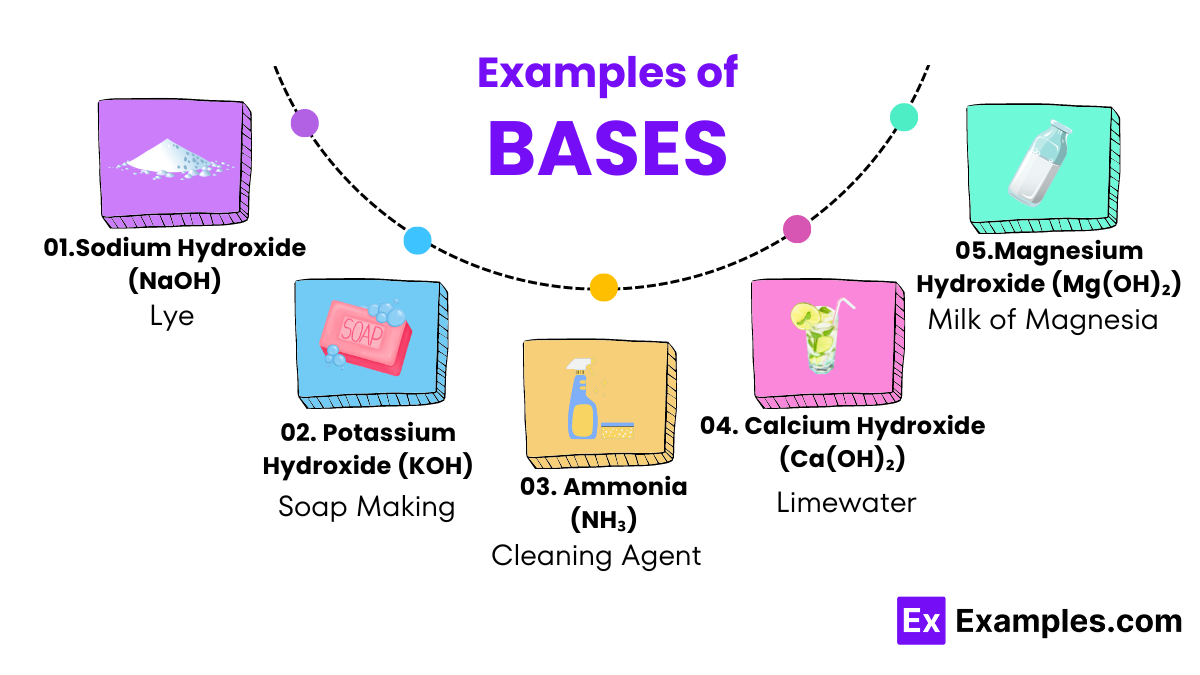
Bases like magnesium hydroxide are used in medicine to neutralize stomach acid and relieve heartburn and indigestion. This is why substances like milk of magnesia are popular over-the-counter treatments for acid-related discomfort.
Calcium hydroxide, often used by farmers, helps to neutralize acidic soils, making them more suitable for growing crops. This process improves soil health and increases agricultural productivity.
Sodium hydroxide is used in food preparation to cure foods like olives, making them less bitter and enhancing their flavor. It is also used in the preparation of pretzels, where it gives the outer crust a unique texture and taste.
Potassium hydroxide is essential in making biodiesel. It acts as a catalyst in the chemical reaction that converts vegetable oils and animal fats into the methyl esters that make up biodiesel, proving crucial for sustainable energy solutions.
Finding a base in chemistry involves understanding its properties and reactions. Bases are substances that can accept hydrogen ions (protons) or donate a pair of valence electrons to form a bond. They have a bitter taste, feel slippery, and turn red litmus paper blue. In a laboratory setting, you can identify a base using indicators like phenolphthalein, which turns pink in a basic solution. Common methods include titration with an acid of known concentration, measuring pH with a pH meter or pH paper, and observing reactions with acidic substances where formation of water and salts occurs.
The title of the strongest base in chemistry goes to substances known as superbases, which are significantly stronger than simple hydroxide ions. One of the most notable examples is ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion. These superbases cannot exist in aqueous solutions as they deprotonate water. In non-aqueous media, however, they exhibit extremely high basicity and can deprotonate even weak acids. Superbases are often used in organic synthesis and research applications to initiate strong nucleophilic reactions where traditional bases would be ineffective.
The pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14, measures how acidic or basic a solution is. The pH of 7 is neutral, indicating neither acidic nor basic qualities. A pH less than 7 indicates acidity, and a pH greater than 7 indicates basicity. A pH of 14 is not the weakest base; it represents the highest level of basicity in aqueous solutions. The confusion might stem from the inverse relationship between the concentration of hydrogen ions and pH level — higher pH means lower hydrogen ion concentration, indicating stronger basic properties, not weaker.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the pH range of a basic solution?
0-3
3-7
7-10
7-14
Which of the following is a common household base?
Hydrochloric acid
Sodium bicarbonate
Acetic acid
Sulfuric acid
What is the chemical formula of sodium hydroxide?
NaOH
NaCl
KOH
NaHCO3
Which of the following is a property of bases?
Sour taste
Slippery feel
Corrosive to metals
Turn blue litmus paper red
Which base is commonly used in soap making?
Potassium nitrate
Sodium chloride
Sodium hydroxide
Ammonium sulfate
What is the pH of pure water?
What is the pH of pure water?
7
9
11
Which of the following is a strong base?
Ammonia
Sodium hydroxide
Acetic acid
Citric acid
Which of the following bases is used in antacids to neutralize stomach acid?
Magnesium hydroxide
Hydrochloric acid
Sulfuric acid
Phosphoric acid
What is the common name for calcium hydroxide?
Baking soda
Limewater
Vinegar
Bleach
Which base is commonly found in drain cleaners?
Sodium chloride
Potassium nitrate
Sodium hydroxide
Ammonium sulfate
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

