What is the molecular formula of formaldehyde?
CH₄O
CH₂O
C₂H₄O
CH₃OH

Formaldehyde is a fascinating substance that plays a big role in the world of chemistry. At its core, it’s a simple molecular compound, known scientifically as CH₂O. This means it’s made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms arranged in a specific way. Even though it might sound complex, it’s actually found in everyday life, from preserving biological specimens to being used in making various household products. Its unique properties make it incredibly useful, but also something that chemists handle with care due to its strong odor and effects on health. So, when we dive into the chemistry of formaldehyde, we’re exploring a molecule that’s small in size but huge in impact!
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | HCHO |
| Hill formula | CH₂O |
| Name | Formaldehyde |
| Alternate Names | Formalin, Formol, Superlysoform |
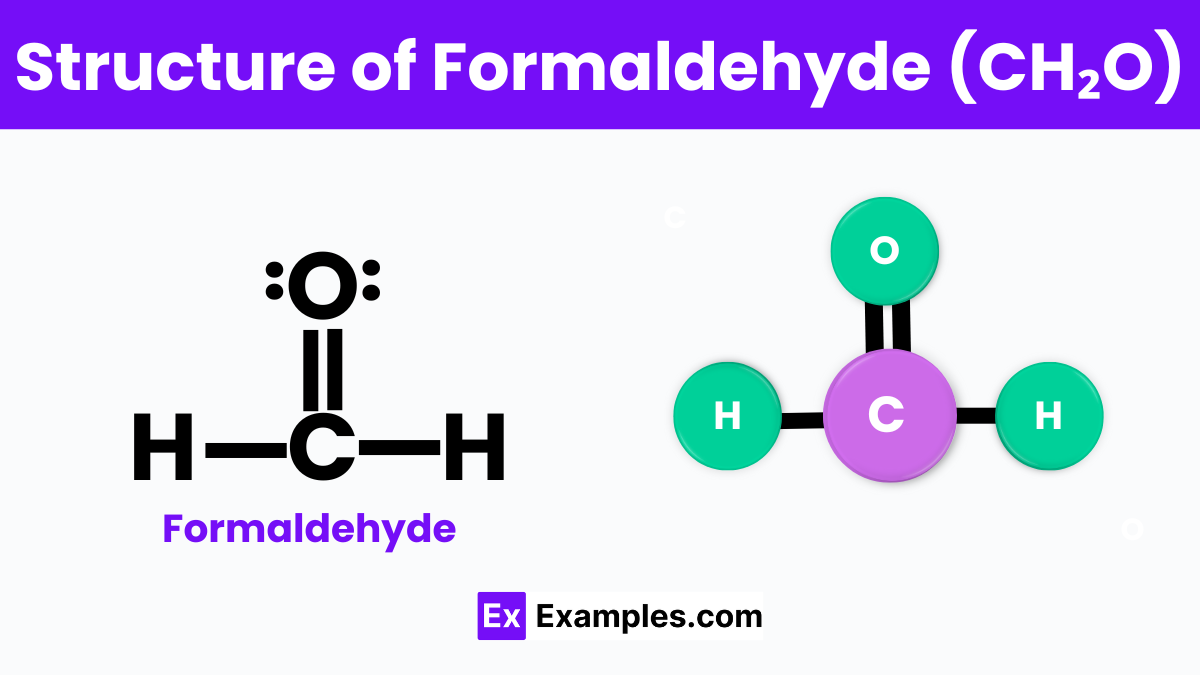
Formaldehyde, a common chemical in the science world, has a simple yet interesting structure that’s easy to understand. Picture it as a central carbon atom (C) holding hands with two hydrogen atoms (H) on one side and forming a double bond with an oxygen atom (O) on the other. This double bond with oxygen is what makes formaldehyde special. It looks like the letter “V,” with the carbon atom at the bottom point. This V-shaped molecule is not only easy to picture but also crucial for its ability to combine with other substances, leading to its wide use in making resins, plastics, and textiles. Understanding the basic “V” structure of formaldehyde helps us see how it fits into so many parts of our daily lives, from the construction of our homes to the clothes we wear.
Formaldehyde is like a magic trick in the world of chemistry, created through a fascinating process. The main method to make formaldehyde is by using a gas called methanol, which scientists turn into formaldehyde through a reaction with oxygen from the air. Imagine methanol as a little building block that, when it meets oxygen, transforms into formaldehyde and water as a byproduct. This transformation happens in the presence of a catalyst, a special substance that speeds up the reaction without being consumed by it.The chemical equation for this process is quite straightforward:
This means two molecules of methanol (CH₃OH) react with one molecule of oxygen (O₂), resulting in two molecules of formaldehyde (CH₂O) and two molecules of water (H₂O). This process is widely used in industries to create formaldehyde, which then goes on to be a part of many products we use every day, from building materials to textiles. Understanding this reaction gives us a glimpse into the fascinating world of chemical transformations.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless gas; it’s invisible in the air and has a very strong, pungent smell that is easily noticeable. |
| Chemical Formula | CH₂O; This shows that formaldehyde is made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms in a specific arrangement. |
| State at Room Temperature | Gas; Formaldehyde is usually found as a gas at room temperature, making it present in the air around us, especially indoors. |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble; It dissolves easily in water, which means it can mix well with water without separating. |
| Boiling Point | -19°C (-2.2°F); This is the temperature at which formaldehyde changes from a liquid to a gas. It has a low boiling point, indicating it turns into a gas at temperatures lower than water does. |
| Melting Point | -92°C (-133.6°F); This is the temperature at which formaldehyde changes from a solid to a liquid. It shows that formaldehyde freezes at a much colder temperature compared to water. |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 50-00-0 |
| Beilstein Number | 1209228 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 712 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 3367 |
| SMILES Identifier | C=O |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/CH2O/c1-2/h1H2 |
| InChI Key | WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYAT |
| MDL Number | MFCD00003274 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 2 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
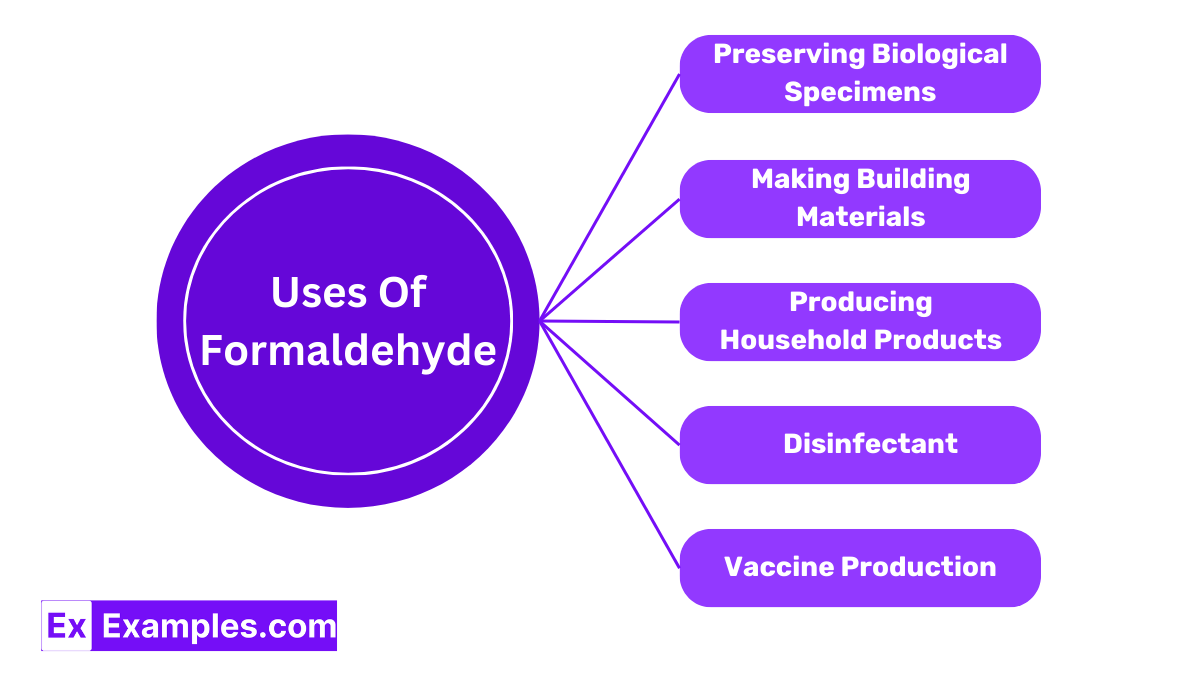
In science labs, formaldehyde is often used as a preservative. It helps keep biological specimens, like frogs or plants, in their original state for a long time, making it easier for students and researchers to study them.
Formaldehyde plays a crucial role in producing building materials, including particleboard, plywood, and fiberglass insulation. It acts as a binder, helping these materials hold their shape and maintain their strength.
Many household products, such as glues, paints, and even some cosmetics, contain formaldehyde. It helps these products perform better, like making glues more adhesive or ensuring paints dry properly.
Formaldehyde is used in treating fabrics to prevent wrinkles and reduce mildew. This means your clothes can look crisp and fresh without needing to iron them frequently.
Due to its ability to kill bacteria and fungi, formaldehyde is also used in some disinfectants and household cleaners. This makes it valuable in maintaining cleanliness and hygiene in various settings.
Interestingly, formaldehyde has a role in creating certain vaccines. It inactivates viruses, making them safe to use in vaccines that help our bodies build immunity without causing the disease.
Formaldehyde exposure can irritate the skin, eyes, nose, and throat, potentially leading to respiratory issues and worsening asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Yes, formaldehyde is harmful, especially with prolonged exposure. It can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, and is linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.
Formaldehyde is found in pressed wood products, glues, paints, fabrics, and cosmetics, particularly in poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
Everyday items containing formaldehyde include pressed wood furniture, adhesives, certain fabrics, and cosmetics like nail polish and hair smoothing products.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the molecular formula of formaldehyde?
CH₄O
CH₂O
C₂H₄O
CH₃OH
Formaldehyde is primarily used in which industry?
Food
Textile
Plastics
Pharmaceuticals
What type of organic compound is formaldehyde?
Alcohol
Ketone
Aldehyde
Carboxylic acid
Which process is used to produce formaldehyde industrially?
Oxidation of methane
Oxidation of methanol
Reduction of methanol
Reduction of methane
What is the common use of formaldehyde in laboratories?
As a solvent
As a preservative
As a reactant
As an acid
Which of the following best describes the structure of formaldehyde?
Linear
Tetrahedral
Planar
Pyramidal
Formaldehyde is classified as which type of hazardous substance?
Carcinogen
Allergen
Mutagen
Teratogen
What is the IUPAC name for formaldehyde?
Methanal
Methanol
Methyl aldehyde
Methyl alcohol
What is the boiling point of formaldehyde?
-19°C
-0.4°C
19°C
41°C
What is the main adverse health effect of formaldehyde exposure?
Skin rash
Respiratory irritation
Digestive issues
Headache
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

