What is the common name for Magnesium Hydroxide in medicine?
Epsom salt
Milk of magnesia
Baking soda
Borax

Magnesium Hydroxide is a compound in chemistry that belongs to the category of bases. It’s made up of magnesium, a shiny gray metal found in many minerals, and hydroxide, a combination of hydrogen and oxygen ions. When magnesium reacts with water or an acid, it forms magnesium hydroxide. This compound is commonly known as milk of magnesia and is often used in medicines to treat indigestion and heartburn because of its ability to neutralize stomach acids. Additionally, magnesium hydroxide is used in various industrial processes, such as water treatment and as a flame retardant in plastics.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | Mg(OH)₂ |
| Hill Formula | H₂MgO₂ |
| Name | Magnesium hydroxide |
| IUPAC Name | Magnesium dihydroxide |
| Alternate Names | Magnesia magma, Magnesia, Magnesium dihydroxide, Magnesium hydrate , Milk of magnesia |
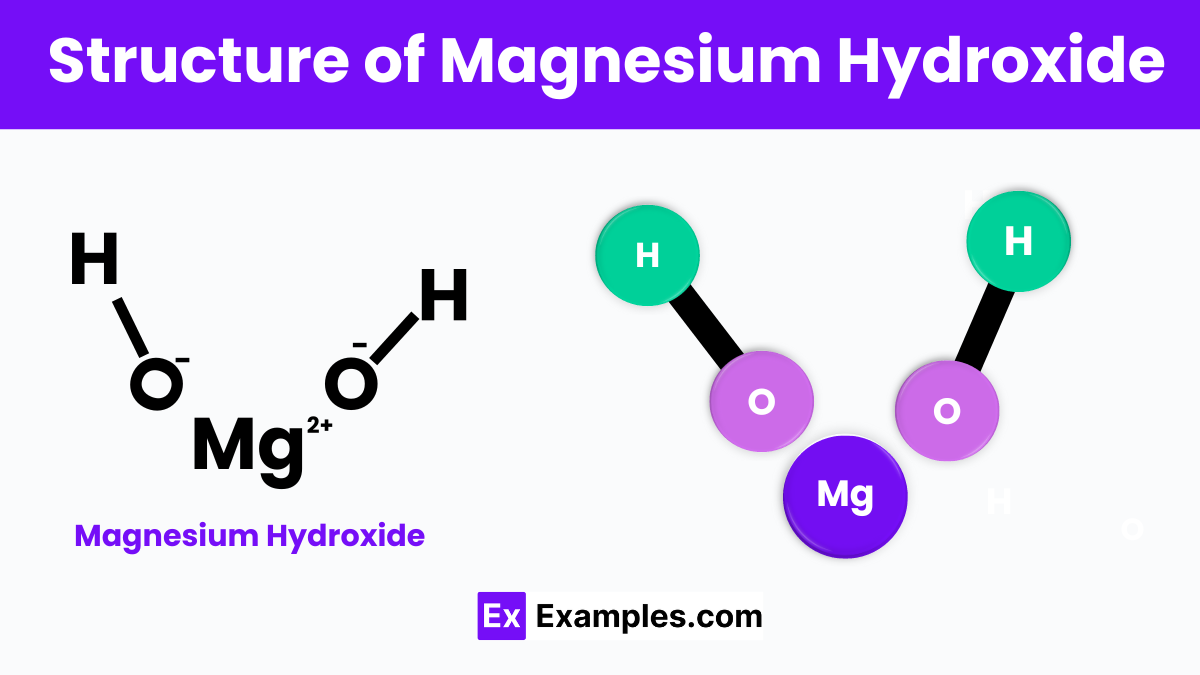
Magnesium Hydroxide is composed of magnesium ions (Mg²⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻) arranged in a specific pattern. In its solid form, this compound forms layers where each magnesium ion is surrounded by six hydroxide ions, creating a sheet-like structure. These layers are held together by ionic bonds, which are forces of attraction between positively charged magnesium and negatively charged hydroxide ions. This arrangement results in a stable, crystalline structure that is typical of many minerals found in nature.
Magnesium hydroxide can be prepared using a simple chemical reaction involving magnesium chloride (MgCl₂) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). When these two compounds are mixed in water, they react to form magnesium hydroxide and sodium chloride (table salt). The chemical equation for this reaction is:
In this reaction, the magnesium chloride solution is gradually mixed with a solution of sodium hydroxide. As they react, magnesium hydroxide, which is only slightly soluble in water, forms as a white, solid precipitate. This precipitate can then be separated from the remaining liquid by filtration or settling and drying. This method is commonly used in laboratories and industrial processes to produce magnesium hydroxide for various applications, including medical uses and as a fire retardant.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, odorless powder |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble, more soluble in water containing CO₂ |
| Density | 2.34 grams per cubic centimeter |
| Melting Point | Decomposes at about 350°C (does not melt) |
| Boiling Point | Not applicable as it decomposes before boiling |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low, similar to other ceramic materials |
| pH | Highly alkaline (around 10.5 in a saturated solution) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1309-42-8 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 14791 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24882320 |
| SMILES Identifier | [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/Mg.2H2O/h;21H2/q+2;;/p-2/fMg.2HO/h;21h/qm;2*-1 |
| RTECS Number | OM3570000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00011104 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 1 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 0 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
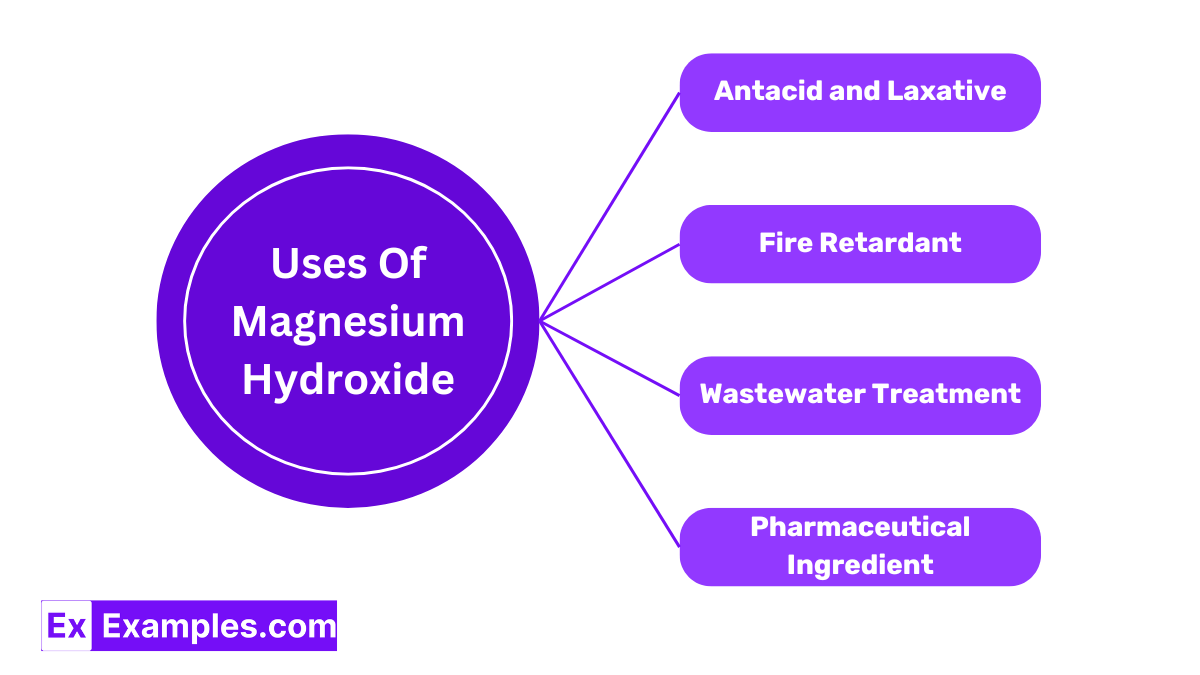
Magnesium Hydroxide is widely used as an antacid to relieve heartburn, upset stomach, and indigestion by neutralizing stomach acid. It also acts as a laxative to alleviate constipation. Its gentle action on the bowels makes it a popular choice for regular use, helping to maintain digestive comfort.
In the production of materials that require fire resistance, Magnesium Hydroxide is used as a fire retardant. It decomposes at high temperatures to release water vapor, which helps to cool and slow the spread of fire, making it an essential component in safety equipment and construction materials.
Magnesium Hydroxide is employed in environmental applications, particularly in the treatment of wastewater. It adjusts the pH of waste water to neutralize acids and remove heavy metals through precipitation, improving the safety and cleanliness of water before it is released back into the environment.
Magnesium Hydroxide is used as an ingredient in various products, including antiperspirants and skin care items. Its ability to neutralize acid and soothe makes it beneficial in formulations designed to reduce body odor and treat skin conditions.
Yes, It is safe for humans when used as directed for relieving indigestion and constipation.
It acts as an antacid and laxative, easing heartburn, indigestion, and constipation effectively.
Individuals with kidney disease, severe abdominal pain, or dehydration.
No, it is not cancerous. It is considered safe and is commonly used in medical treatments.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the common name for Magnesium Hydroxide in medicine?
Epsom salt
Milk of magnesia
Baking soda
Borax
What is the primary use of Magnesium Hydroxide in the pharmaceutical industry?
Pain reliever
Antacid and laxative
Antibiotic
Antihistamine
Which property of Magnesium Hydroxide makes it effective as an antacid?
Basic nature
Neutral pH
Amphoteric nature
Acidic nature
What is the solubility of Magnesium Hydroxide in water?
Highly soluble
Moderately soluble
Insoluble
Sparingly soluble
What is the color of Magnesium Hydroxide in its pure form?
White
Yellow
Blue
Green
Which of the following industries uses Magnesium Hydroxide as a flame retardant?
Textile
Food processing
Construction
Electronics
Magnesium Hydroxide is used in wastewater treatment for what purpose?
To increase acidity
To increase turbidity
To neutralize acidity
To promote bacterial growth
What is the primary effect of Magnesium Hydroxide when ingested as a laxative?
Absorbs water from the intestines
Stimulates the stomach lining
Draws water into the intestines
Increases bile production
Which of the following is NOT a property of Magnesium Hydroxide?
White solid
High solubility in water
Basic nature
Neutralizes acids
In which of the following products is Magnesium Hydroxide commonly found?
Toothpaste
Shampoo
Sunscreen
Deodorant
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

