What is the primary role of chlorophyll in plants?
To absorb nutrients
To capture light energy
To produce flowers
To transport water


Chlorophyll is a vital compound found in plants, giving them their characteristic green color. As a crucial component in the process of photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and converts it into energy, which plants use to grow. This complex compound plays a central role in the chemistry of life, helping plants produce oxygen, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms on Earth. Understanding chlorophyll and its function is fundamental in studies of plant biology and ecology.
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll a is the most common type of chlorophyll found in green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. It is essential for photosynthesis as it primarily absorbs light in the blue-violet and red parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. This pigment directly participates in the conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
Chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll b is another type of chlorophyll found in green plants and green algae. It complements chlorophyll a by absorbing light in the blue and red-orange light spectra, which chlorophyll a does not absorb as efficiently. This broader range of light absorption enhances the overall efficiency of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll c
Chlorophyll c can be found in certain groups of marine algae, including diatoms and dinoflagellates. Unlike chlorophyll a and b, chlorophyll c assists in capturing light in deeper or murkier water conditions, extending the range of light that contributes to photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll d
Chlorophyll d is primarily found in red algae and is adapted to absorb far-red light, which penetrates deeper into water than the light other chlorophylls absorb. This adaptation allows red algae to photosynthesize in deeper waters where light conditions are very different.
Chlorophyll e
Although not as commonly discussed, recent studies suggest the presence of chlorophyll e in some types of algae. This pigment helps these organisms adapt to extreme environments and varied light conditions, although research is still ongoing to fully understand its properties and functions.
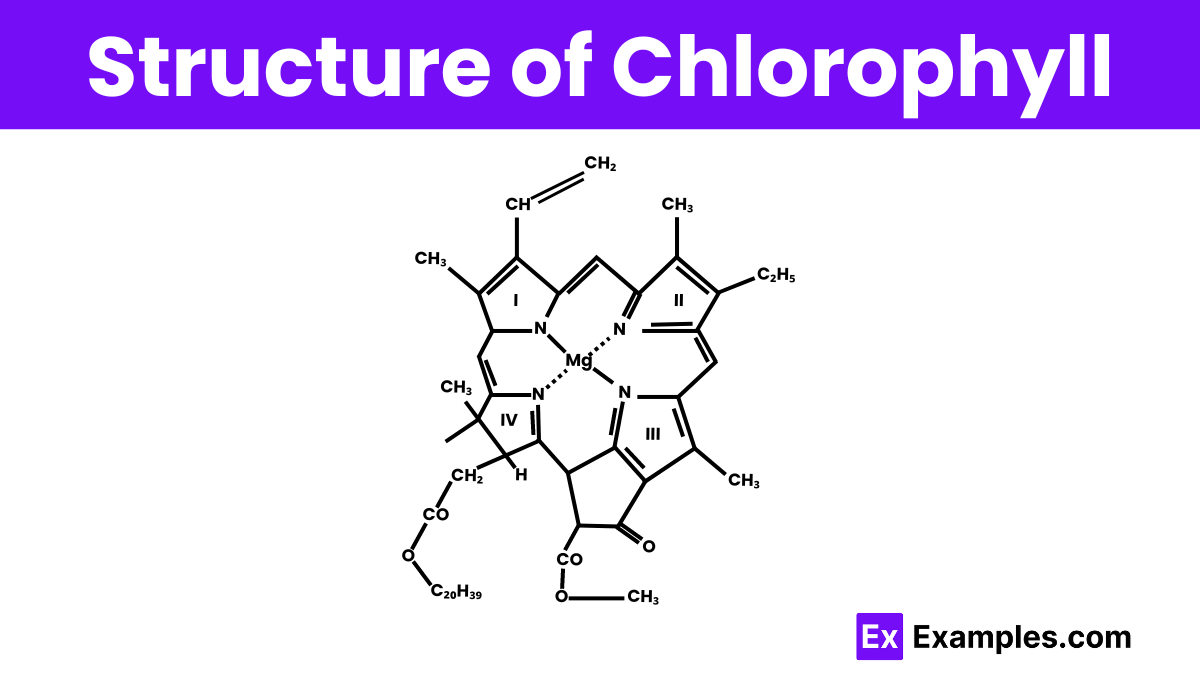
Chlorophyll has a complex structure that is key to its function in photosynthesis. At the center of chlorophyll is a magnesium ion, which is held in a large ring structure known as a porphyrin. This ring includes alternating double bonds that are crucial because they allow chlorophyll to absorb light at various wavelengths. Attached to the porphyrin ring is a long, hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail, which helps chlorophyll anchor itself within the lipid membranes of plant cells. This positioning is vital for chlorophyll’s role in capturing sunlight and converting it into energy. The structure of chlorophyll is perfectly suited to capture light and initiate the process of energy production in plants.
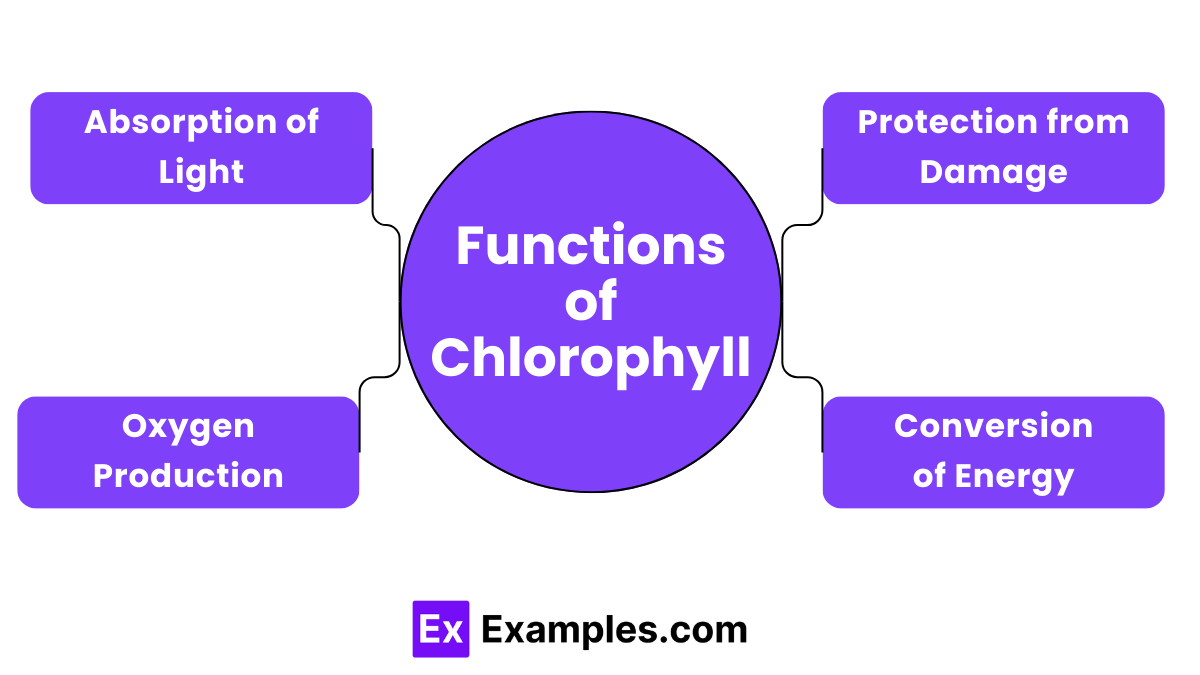
Chlorophyll’s primary function is to absorb light, primarily from the blue and red parts of the spectrum, which is essential for photosynthesis. This process allows plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, which they use to fuel their growth and development.
Once chlorophyll absorbs sunlight, it converts this solar energy into a usable form of chemical energy. It does this by transferring the energy to other molecules in the plant, initiating the synthesis of sugars from carbon dioxide and water.
During photosynthesis, chlorophyll plays a crucial role in splitting water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen. The oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, which is vital for the survival of most life forms on Earth.
Chlorophyll also helps protect plants from excess light and oxidative damage. By converting absorbed light into energy, it prevents the buildup of harmful reactive oxygen species that can damage plant tissues.
Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their own food. This process not only sustains the plant’s growth and survival but also produces oxygen, which is crucial for most life forms on Earth.
Chlorophyll promotes plant health by enabling efficient energy conversion. Healthy, green plants are more capable of resisting diseases and pests, leading to better growth and productivity.
By facilitating photosynthesis, chlorophyll plays a significant role in oxygen production. More chlorophyll in plants means more oxygen released into the atmosphere, which improves air quality and supports aerobic life forms.
Chlorophyll has potential health benefits for humans as well, including promoting wound healing and detoxification. It’s often used as a natural supplement to improve overall health due to its antioxidant properties.
Chlorophyll helps detoxify the body by binding toxins and heavy metals, facilitating their expulsion. This supports better liver health and overall wellness.
Chlorophyll’s antiseptic properties accelerate wound healing by reducing inflammation and killing bacteria, aiding the body’s natural healing processes.
Chlorophyll acts as a natural deodorizer, combating bad breath and body odor by cleansing the body and reducing odor-causing compounds.
Chlorophyll fights free radicals, harmful molecules that can damage cells, protecting against various diseases, including some cancers.
Chlorophyll consumption often leads to increased energy levels, possibly by improving the quality of red blood cells.
Chlorophyll primarily absorbs light in the blue-violet and red parts of the spectrum, essential for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll cannot produce electricity directly, but it converts solar energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Human cells cannot use chlorophyll for photosynthesis, but it has health benefits when consumed, like detoxification and wound healing.
Individuals with sensitivity to chlorophyll or those on medication should consult a doctor before consuming chlorophyll supplements.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary role of chlorophyll in plants?
To absorb nutrients
To capture light energy
To produce flowers
To transport water
Chlorophyll gives plants their green color. What specific aspect of chlorophyll contributes to this coloration?
Its molecular structure
Its size
Its position in the cell
Its ability to absorb red light
In which part of the plant cell is chlorophyll primarily located?
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Ribosomes
What happens to chlorophyll during the fall season in deciduous trees?
It becomes more active
It stays green
It breaks down and fades
It turns red
Which wavelengths of light are primarily absorbed by chlorophyll for photosynthesis?
Green and yellow
Blue and red
Orange and purple
Infrared and ultraviolet
Chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b are types of chlorophyll. What is a key difference between them?
They absorb different wavelengths of light
They are found in different types of plants
They have different roles in cellular respiration
They are located in different parts of the chloroplast
What effect does chlorophyll have on the energy of light?
It reflects all light energy
It absorbs light energy and converts it into chemical energy
It blocks light energy from entering the cell
It dissipates light energy as heat
In which type of organism is chlorophyll found besides plants?
Animals
Fungi
Algae
Bacteria
What would likely happen to a plant if it lacked chlorophyll?
It would grow faster
It would not be able to perform photosynthesis
It would produce more flowers
It would change color to red
What is the role of chlorophyll in the photosynthesis process?
It converts carbon dioxide into oxygen
It captures light energy to drive the synthesis of sugars
It transports nutrients to the plant
It provides structural support to the plant
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

