What is the molecular formula of ethylene?
C₂H₂
C₂H₄
C₃H₆
C₂H₆

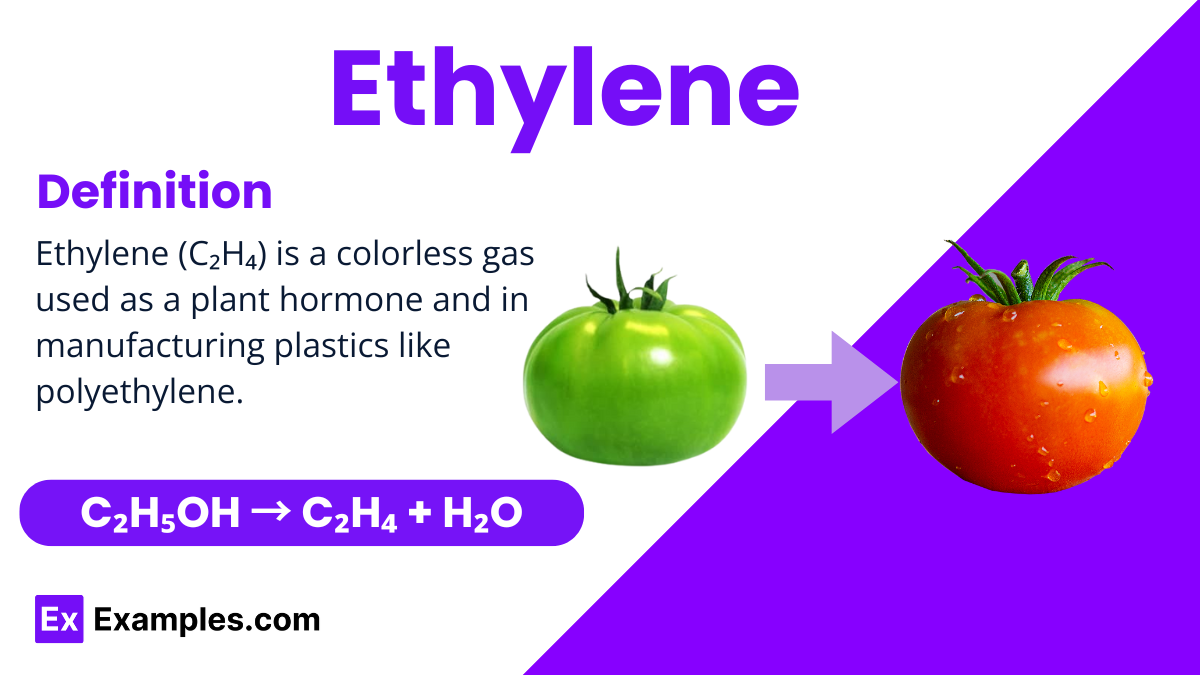
Ethylene is an Organic Compound and it is a colorless gas widely recognized for its simple structure and significant role in the natural world and industry. It is a hydrocarbon, which means it is made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms, specifically with the chemical formula C₂H₄. This compound is particularly notable for being the smallest alkene, which is a type of hydrocarbon with a carbon-carbon double bond in its structure. In nature, plants produce ethylene as a hormone that influences growth and development, such as the ripening of fruits. Industrially, ethylene is crucial in the production of plastics, antifreeze, and other synthetic materials. Its applications make it a fundamental substance in both biological and manufacturing processes.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | CH₂=CH₂ |
| Hill Formula | C₂H₄ |
| Name | Ethylene |
| Alternate Names | Acetene, Elayl, Ethene, Freon 1150, Olefiant Gas, R-1150 |
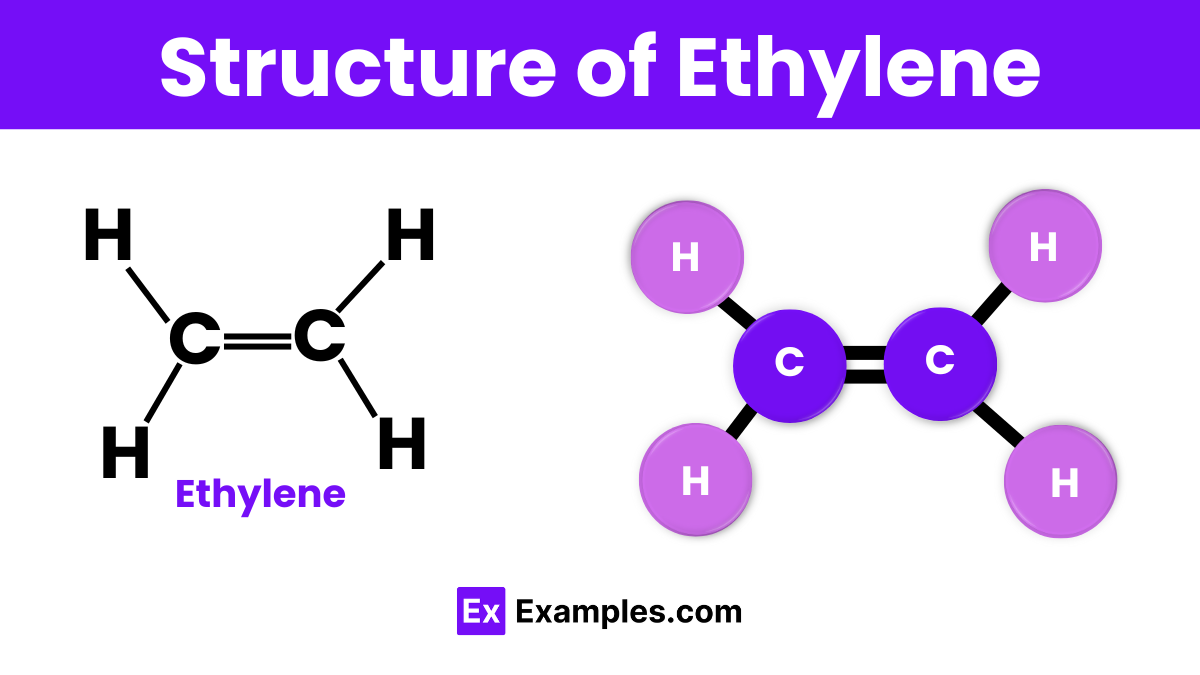
Ethylene, with its chemical formula C₂H₄, features a straightforward molecular structure consisting of two carbon atoms double-bonded to each other. Each carbon atom is also bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This configuration forms a flat, planar molecule, which is characteristic of alkenes—the family of hydrocarbons that ethylene belongs to. The double bond between the carbon atoms is key to ethylene’s reactivity and is crucial for its role in chemical synthesis and biological functions. Understanding this structure helps explain why ethylene is so effective in processes like fruit ripening and the production of plastics.
Ethylene can be produced through several methods, but one common laboratory method is the dehydration of ethanol by heating it in the presence of an acid catalyst like sulfuric acid. This process involves heating ethanol with a concentrated acid, which acts to remove water (H₂O) from the ethanol molecule, leaving ethylene. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
In industrial settings, C₂H₄ (Ethylene) is primarily produced by the steam cracking process where hydrocarbons such as ethane and propane are heated to high temperatures. This breaks the larger molecules down into simpler molecules like C₂H₄ (Ethylene). This method is highly efficient and accounts for the majority of ethylene produced globally, which is then used to manufacture a variety of chemical products and materials.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Phase at Room Temperature | Gas |
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Slightly sweet |
| Density | Lighter than air, 1.178 kg/m³ (at 0°C and 1 atm) |
| Boiling Point | -103.7°C |
| Melting Point | -169.2°C |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble |
| Flammability | Highly flammable |
| Identifier | Number/ID |
|---|---|
| CAS registry number | 74-85-1 |
| Beilstein number | 1730731 |
| PubChem compound ID | 6325 |
| PubChem substance ID | 24857774 |
| SMILES identifier | C=C |
| InChI identifier | InChI=1/C2H4/c1-2/h1-2H2 |
| RTECS number | KU5340000 |
| MDL number | MFCD00008604 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA health rating | 1 |
| NFPA fire rating | 4 |
| NFPA reactivity rating | 0 |
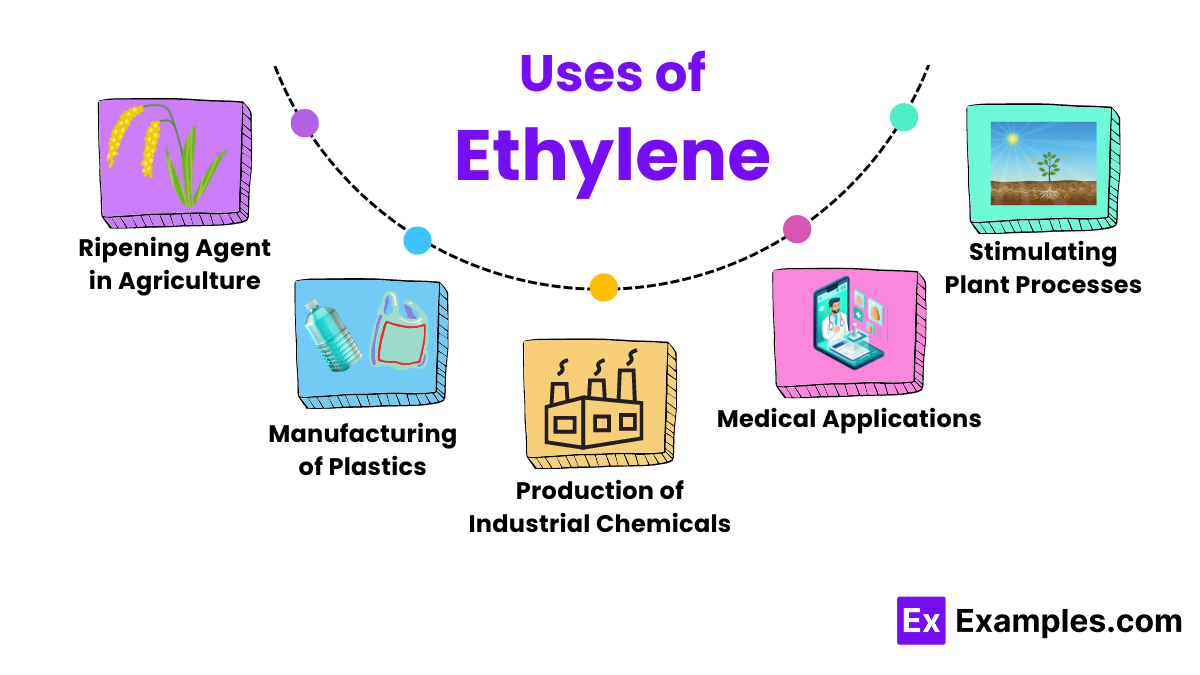
Ethylene is widely used in agriculture to regulate the ripening of fruits. By controlling the application of ethylene, farmers and distributors can ensure fruits such as bananas, tomatoes, and apples reach peak ripeness at the right time, enhancing flavor and texture for consumers.
One of the most significant uses of ethylene is in the production of polyethylene, one of the most common plastics used today. This plastic is utilized in products ranging from plastic bags and containers to more durable items like pipes and fittings.
Ethylene is a key raw material for producing other chemicals including ethylene oxide and ethylene glycol. Ethylene oxide is crucial in making antifreeze and detergents, while ethylene glycol is used in the production of polyester fibers and resin.
In horticulture, ethylene is used to stimulate various plant processes such as flowering and the shedding of leaves. This application helps in managing the life cycle of plants more effectively in commercial nurseries and gardens.
Ethylene is also used in the medical field, particularly in the synthesis of medical products like sterilization agents. Ethylene oxide is used to sterilize surgical instruments and supplies that cannot withstand high temperatures. They are free from microbes without damage.
Ethylene is generally non-toxic at low concentrations but can pose health risks at high levels, causing dizziness and nausea.
Ethylene is not banned; however, its use is regulated due to its flammability and potential health effects at high concentrations.
Ethylene is essentially odor less to humans. However, it has a faintly sweet smell at very high concentrations, which is rarely detectable.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the molecular formula of ethylene?
C₂H₂
C₂H₄
C₃H₆
C₂H₆
Ethylene belongs to which category of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes
Alkenes
Alkynes
Aromatics
What type of bond exists between the carbon atoms in an ethylene molecule?
Single bond
Double bond
Triple bond
Ionic bond
Which of the following is a common use of ethylene?
Fuel
Solvent
Ripening agent for fruits
Lubricant
What is the boiling point of ethylene at standard atmospheric pressure?
-104°C
-88°C
-42°C
0°C
Ethylene can be obtained from which natural source?
Biomass
Coal
Natural gas
Water
How many sigma and pi bonds are present in an ethylene molecule?
5 sigma, 1 pi
4 sigma, 2 pi
6 sigma, 0 pi
3 sigma, 3 pi
The structural formula of ethylene can be represented as:
H-C≡C-H
H₂C=CH₂
H₃C-CH₃
HC≡CH
Which process is used to produce ethylene industrially?
Electrolysis
Filtration
Crystallization
Steam cracking
In which state of matter is ethylene at room temperature?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

