What is the chemical formula of acetic acid?
HCl
H₂SO₄
CH₃COOH
C₂H₅OH

Acetic acid, commonly recognized for its pivotal role in giving vinegar its sharp flavor and smell, stands as a fundamental covalent compound in both nature and various industries. Its simple, versatile structure, denoted by the chemical formula CH₃COOH, enables it to dissolve in water and organic solvents, making it essential in food preservation, manufacturing plastics, and even in healthcare products. Known for its acidic properties and produced through the fermentation of sugars by bacteria, acetic acid’s presence spans from kitchen pantries to high-grade industrial applications, embodying a bridge between everyday life and chemical innovation.
Acetic acid is a simple, sour-tasting covalent compound that primarily contributes to the distinctive taste and aroma of vinegar, alongside water. When it’s in its pure form, acetic acid appears as a colorless liquid that easily mixes with water, emitting a pungent odor. It comprises of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen elements. Acetic acid holds significant value in various industries, being utilized in the production of plastic materials, food preservatives, and certain pharmaceuticals. It naturally arises through the fermentation process, where bacteria decompose sugars without the presence of oxygen, leading to the creation of this versatile compound.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | CH₃CO₂H |
| Hill Formula | C₂H₄O₂ |
| Name | Acetic Acid |
| Alternate Names | Acetic Acid, Glacial, Ethanoic Acid, Ethylic Acid, Glacial Acetic Acid, Methanecarboxylic Acid, Vinegar Acid |
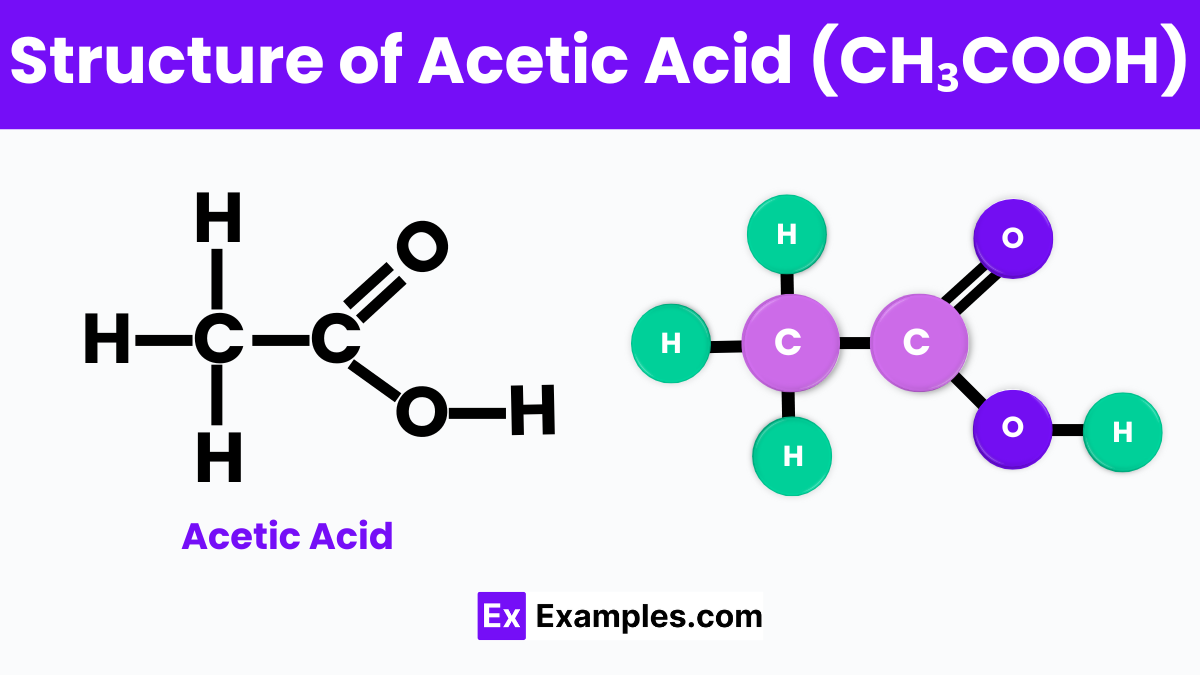
Acetic acid is a small, simple molecule made up of two main parts: a methyl group and a carboxyl group. The methyl group consists of one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, symbolized as CH₃ . This part of the molecule is hydrophobic, which means it does not mix well with water. On the other hand, the carboxyl group is represented as COOH, contains one carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (which is one oxygen atom bonded to one hydrogen atom). The carboxyl group is hydrophilic, meaning it can interact well with water.
This combination of a hydrophobic part and a hydrophilic part gives acetic acid its unique properties, allowing it to dissolve in both water and organic solvents. The carboxyl group is also responsible for acetic acid’s acidic behavior. When acetic acid dissolves in water, it can release a proton (a hydrogen ion,H⁺) from the hydroxyl part of the carboxyl group. This release of a proton is what makes acetic acid an acid, capable of lowering the pH of a solution and giving vinegar its sour taste.
Acetic acid can be made in several ways, but one of the most common methods in the industrial world is through the fermentation of ethanol (alcohol) by bacteria. This process is similar to how vinegar is made on a smaller scale at home or in food production. The equation for this biological reaction is quite straightforward:
In simple terms, this means that ethanol (the alcohol in alcoholic beverages) reacts with oxygen in the air. Under the right conditions, with the help of certain bacteria, it transforms into acetic acid and water.
Another major industrial method for producing acetic acid is through the chemical reaction known as the methanol carbonylation process. In this method, methanol (a type of alcohol) reacts with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst to produce acetic acid. The equation for this process is:
This process is highly efficient and is used to produce a large amount of acetic acid for various uses in industries, from making plastics and textiles to food additives and pharmaceuticals.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pungent, vinegar-like smell |
| Chemical Formula | CH₃COOH |
| State at Room Temperature | Liquid |
| Solubility | Mixes well with water, alcohol, and many other organic solvents |
| Boiling Point | About 118°C (244°F) |
| Melting Point | About 16°C (61°F) |
| Density | 1.049 g/cm³ at 20°C (68°F) |
| pH | Typically around 2.4 in a 1.0 M solution, indicating strong acidity |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.76, showing its strength as an acid |
Acetic acid is a weak acid, which means it partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions H⁺. This property is what gives vinegar its sour taste and enables acetic acid to react with bases to form water and salts.
When acetic acid reacts with metals like magnesium or zinc, it produces hydrogen gas and forms acetate salts. This reaction is typical of acids and metals, showcasing acetic acid’s ability to corrode certain metals.
Acetic acid can react with alcohols in a process called esterification to produce esters and water. Esters are often fragrant compounds used in food flavorings and perfumes. This reaction is important in manufacturing various chemical products.
Due to its polar nature, acetic acid is highly soluble in water, alcohol, and many organic solvents. This property is crucial for its use in food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries, as it can easily mix with other substances.
When heated above its boiling point, acetic acid can decompose into water and either ketene or acetaldehyde, depending on the conditions. This decomposition is significant in the production of other chemicals.
Acetic acid reacts with bases to form acetate salts. It also forms various derivatives, such as acetyl chloride and acetic anhydride, through reactions with different reagents. These compounds are vital in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and synthetic fibers.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 64-19-7 |
| Beilstein Number | 506007 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 176 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 3335 |
| SMILES Identifier | CC(=O)O |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C2H4O2/c1-2(3)4/h1H3, (H, 3, 4)/f/h3H |
| InChI Key | QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-TULZNQERCK |
| RTECS Number | AF1225000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00036152 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 2 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
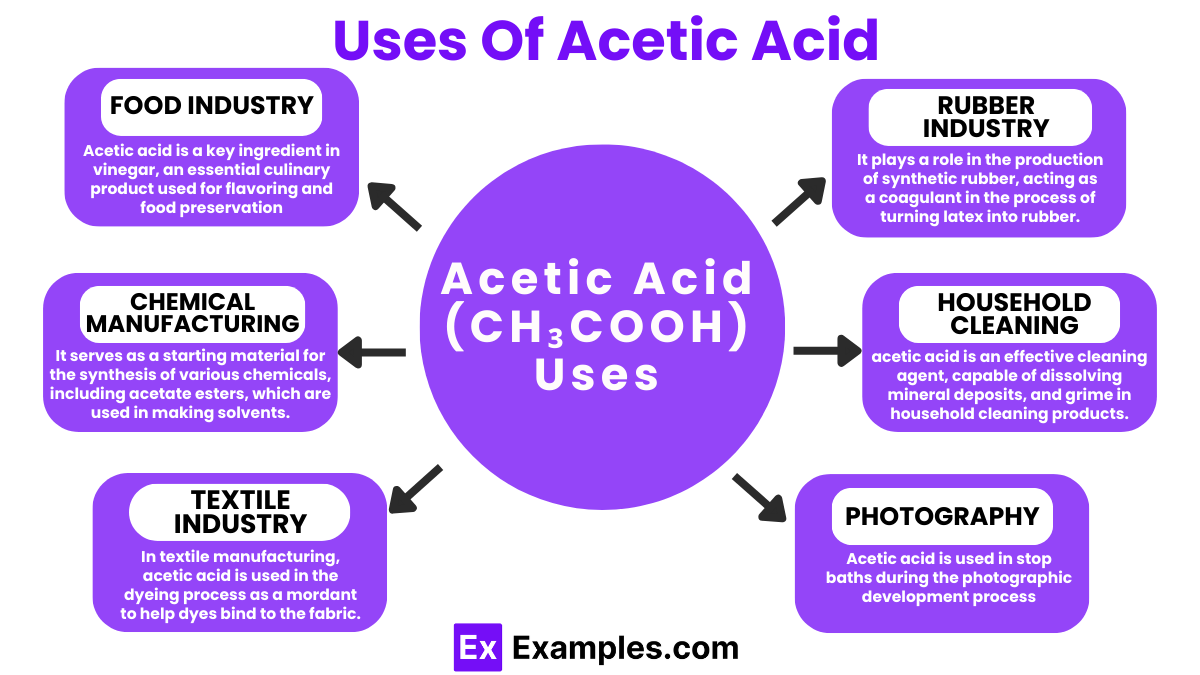
Acetic acid is a key ingredient in vinegar, an essential culinary product used for flavoring and food preservation. Its antibacterial properties make it ideal for pickling vegetables and preparing condiments.
It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of various chemicals, including acetate esters, which are used in making solvents, inks, and coatings.
Acetic acid is used in the production of several medications, including aspirin. It’s valued for its antifungal and antibacterial properties, making it useful in treating ear infections and as an excipient in pharmaceuticals.
In textile manufacturing, acetic acid is used in the dyeing process as a mordant to help dyes bind to the fabric, improving color fastness.
As a herbicide, acetic acid can effectively control weeds in organic farming, offering an eco-friendly alternative to chemical herbicides.
It plays a role in the production of synthetic rubber, acting as a coagulant in the process of turning latex into rubber.
Thanks to its acidic nature, acetic acid is an effective cleaning agent, capable of dissolving mineral deposits, dirt, grease, and grime in household cleaning products.
Acetic acid is used in stop baths during the photographic development process, where its acidity stops the action of the developer.
In moderation, acetic acid can aid in weight management, stabilize blood sugar levels, and support digestion. However, excessive consumption may lead to adverse effects.
Acetic acid can be hazardous if mishandled, causing skin and eye irritation, respiratory issues, and chemical burns at high concentrations. Proper handling is essential.
Vinegar is primarily water mixed with acetic acid, which gives it its characteristic sour taste and aroma. The acetic acid content in vinegar varies by type.
No, white vinegar is not 100% acetic acid. It typically contains 4-7% acetic acid, with the rest being water and trace chemicals.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of acetic acid?
HCl
H₂SO₄
CH₃COOH
C₂H₅OH
Acetic acid is the main component of which common kitchen ingredient?
Baking soda
Vinegar
Salt
Sugar
Which type of chemical reaction does acetic acid undergo when it reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst?
Esterification
Fermentation
Neutralization
Hydrolysis
What is the approximate molar mass of acetic acid?
18 g/mol
46 g/mol
60 g/mol
90 g/mol
Acetic acid is considered:
A strong acid
A weak acid
A strong base
A weak base
In industrial settings, acetic acid is used to manufacture:
Polyester fibers
Acetic anhydride
Sodium bicarbonate
Ethanol
What property of acetic acid makes it a good solvent for organic compounds?
High polarity
Low polarity
High boiling point
Low reactivity
The presence of which functional group in acetic acid is responsible for its acidic nature?
Hydroxyl group
Carbonyl group
Carboxyl group
Amino group
Acetic acid's smell is often described as:
Sweet
Pungent
Bitter
Odorless
What safety hazard is primarily associated with acetic acid?
Explosive
Corrosive
Flammable
Radioactive
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

