What is a function in mathematics?
A relation where every input has one or more outputs.
A relation where every input has exactly one output.
A relation where outputs can have multiple inputs.
A set of numbers without any specific relationship.

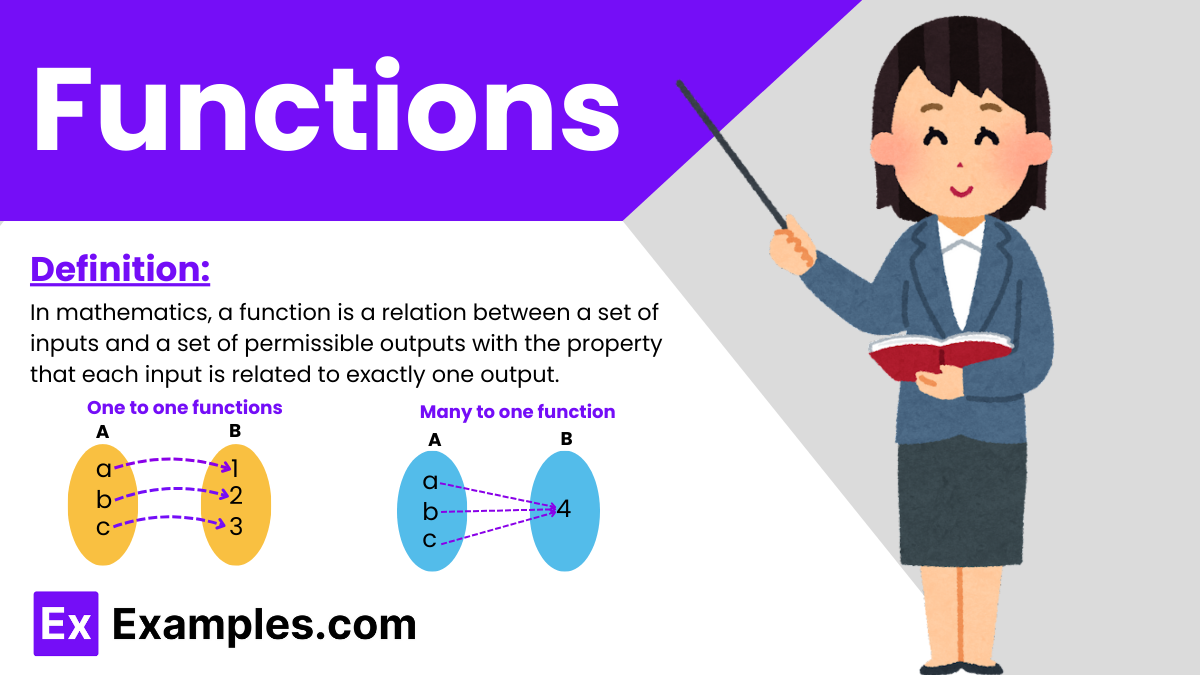
In mathematics, a function is a relation between a set of inputs and a set of permissible outputs with the property that each input is related to exactly one output. Functions are fundamental to many areas of mathematical, scientific, and engineering disciplines, encapsulating the idea of a deterministic relationship where one quantity completely determines another.
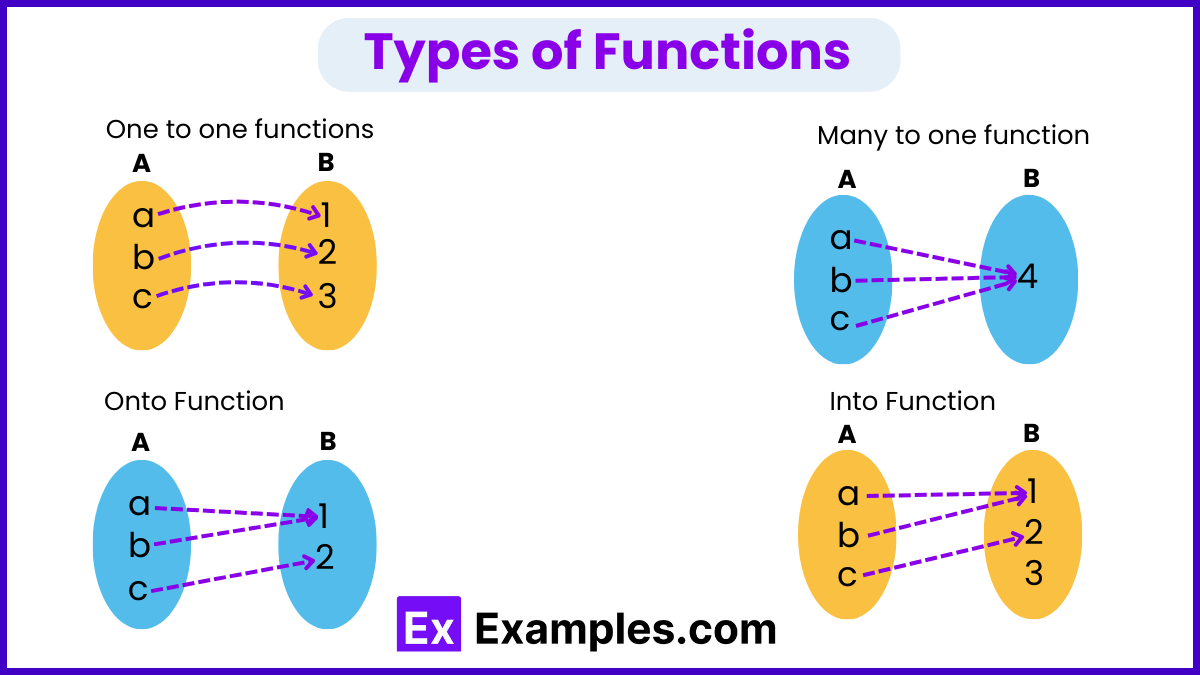
In mathematics, functions can be classified based on how they map elements from the domain (set of all possible input values) to the codomain (set of all potential output values). Understanding these different types of functions is crucial for analyzing mathematical relationships and solving problems across various fields. Here’s an overview of some fundamental types of functions:
A function in algebra is often written as 𝑓(𝑥), where 𝑓 denotes the function and x represents the input variable. The output of the function, 𝑓(𝑥), depends on the input value 𝑥.
f(x) = anxn + an – 1xn – 1+ an-2xn-2+ ……. ax + c.
For example:
| Type | Functions |
|---|---|
| Based on Mapping | |
| One One Function | Maps each element of the domain to a unique element in the codomain. |
| Many One Function | Maps multiple elements of the domain to a single element in the codomain. |
| Onto Function | Covers every element of the codomain. |
| One One and Onto Function | Bijective function, both one-to-one and onto. |
| Into Function | Does not map to every element of the codomain. |
| Based on Degree | |
| Constant Function | Outputs the same value for any input. |
| Identity Function | Outputs the input itself. |
| Linear Function | First-degree polynomial with no exponents or powers greater than one. |
| Quadratic Function | Second-degree polynomial. |
| Cubic Function | Third-degree polynomial. |
| Polynomial Functions | Functions that can be represented by polynomials. |
| Based on Math Concepts | |
| Algebraic Functions | Functions involving polynomial expressions. |
| Trigonometric Functions | Functions involving angles and ratios of triangle sides. |
| Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Functions that reverse trigonometric functions. |
| Logarithmic and Exponential Functions | Functions involving logarithms and exponents. |
| Miscellaneous Functions | |
| Modulus Function | Outputs the absolute value of the input. |
| Rational Function | Ratio of two polynomial functions. |
| Signum Function | Indicates the sign of a number. |
| Even and Odd Functions | Symmetric functions relative to the y-axis or origin. |
| Periodic Functions | Functions that repeat their values at regular intervals. |
| Greatest Integer Function | Rounds down to the nearest integer. |
| Inverse Function | Reverses another function. |
A function 𝑓(𝑥) can be visualized on a graph by plotting points that represent the relationship between each input value 𝑥 and its corresponding output 𝑦=𝑓(𝑥). To create this graph, you select various values for 𝑥, compute the corresponding 𝑦 values, and then plot these (x, y) pairs on a coordinate plane. Here’s an illustrative example:
Suppose, y = x + 3
Then,
The six fundamental trigonometric functions are defined as follows: 𝑓(𝜃)=sin𝜃, 𝑓(𝜃)=cos𝜃, 𝑓(𝜃)=tan𝜃, 𝑓(𝜃)=sec𝜃, 𝑓(𝜃)=csc𝜃, and 𝑓(𝜃)=cot𝜃. Here, the domain variable 𝜃 represents an angle, which can be measured in either degrees or radians. These trigonometric functions are derived from the ratios of the sides of a right triangle and are fundamentally linked to the principles of the Pythagorean theorem
A function defines a specific relationship where each input has a single output. It’s a way to express one quantity as dependent on another.
Functions are described by their rules, domain (inputs), and range (outputs). They map each element of the domain to one element in the range.
When something is a function of something else, it means that the first variable’s value depends on the second. Changes in the second variable directly affect the first.
A real-life example of a function is the relationship between distance traveled and time in a car where speed is constant, described as 𝑑=𝑣𝑡.
An example of a simple function is 𝑓(𝑥)=𝑥2, which squares the input value to produce the output.
A function in mathematics is like a machine: you input a number, it performs a set rule (like multiplication or addition), and then outputs a new number based on that rule.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is a function in mathematics?
A relation where every input has one or more outputs.
A relation where every input has exactly one output.
A relation where outputs can have multiple inputs.
A set of numbers without any specific relationship.
Which of the following is a characteristic of a function?
Each input value must map to multiple output values.
Each output value must have multiple input values.
Each input value must map to exactly one output value.
Each output value must map to exactly one input value.
If \( f(x) = 2x + 3 \), what is \( f(4) \)?
9
10
11
12
Which statement describes the function \( f(x) = x^2 \)?
It maps each input to its square.
It maps each input to its square root.
It maps each input to the reciprocal of the input.
It maps each input to its double.
What does the domain of a function refer to?
The set of all possible output values.
The set of all possible input values.
The set of all possible pairs of input and output values.
The relationship between the input and output values.
For the function \( f(x) = \frac{1}{x} \), what is the domain?
All real numbers except 0.
All real numbers.
All positive real numbers.
All negative real numbers.
If \( f(x) = 3x - 5 \), which of the following is the output when \( x = 2 \)?
4
5
6
7
What is the range of the function \( f(x) = x^2 + 2 \)?
All real numbers.
All real numbers greater than or equal to 2.
All real numbers less than or equal to 2.
All positive real numbers.
Which of the following functions is a one-to-one function?
\( f(x) = x^2 \)
\( f(x) = 2x + 1 \)
\( f(x) = \frac{1}{x} \)
\( f(x) = x^2 - 1 \)
What is the inverse of the function \( f(x) = 3x + 4 \)?
\( f^{-1}(x) = \frac{x - 4}{3} \)
\( f^{-1}(x) = \frac{x + 4}{3} \)
\( f^{-1}(x) = \frac{x - 3}{4} \)
\( f^{-1}(x) = \frac{x - 3}{2} \)
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

