What is the molecular formula of acetone?
C₂H₄O
C₃H₆O
C₃H₈O
C₄H₈O₂


Acetone is organic compound and it has a clear, highly flammable liquid that is widely known for its versatility and effectiveness as a solvent. It is commonly used in everyday life, especially in nail polish remover and in various cleaning products. Chemically, acetone is the simplest form of ketone, a compound characterized by a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom, with two additional carbon atoms attached. Acetone evaporates quickly and has a distinct, sweet smell. It is also produced naturally in the human body during the breakdown of fat. Due to its ability to dissolve many other substances, acetone is a valuable tool in scientific labs and industries.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | CH₃COCH₃ |
| Hill Formula | C₃H₆O |
| Name | Acetone |
| Alternate Names | 2-Propanone, Dimethylketal, Dimethyl Ketone, Ketone, Dimethyl-, Ketone Propane, Methyl Ketone, Propan-2-one, Propanone, Pyroacetic Ether |
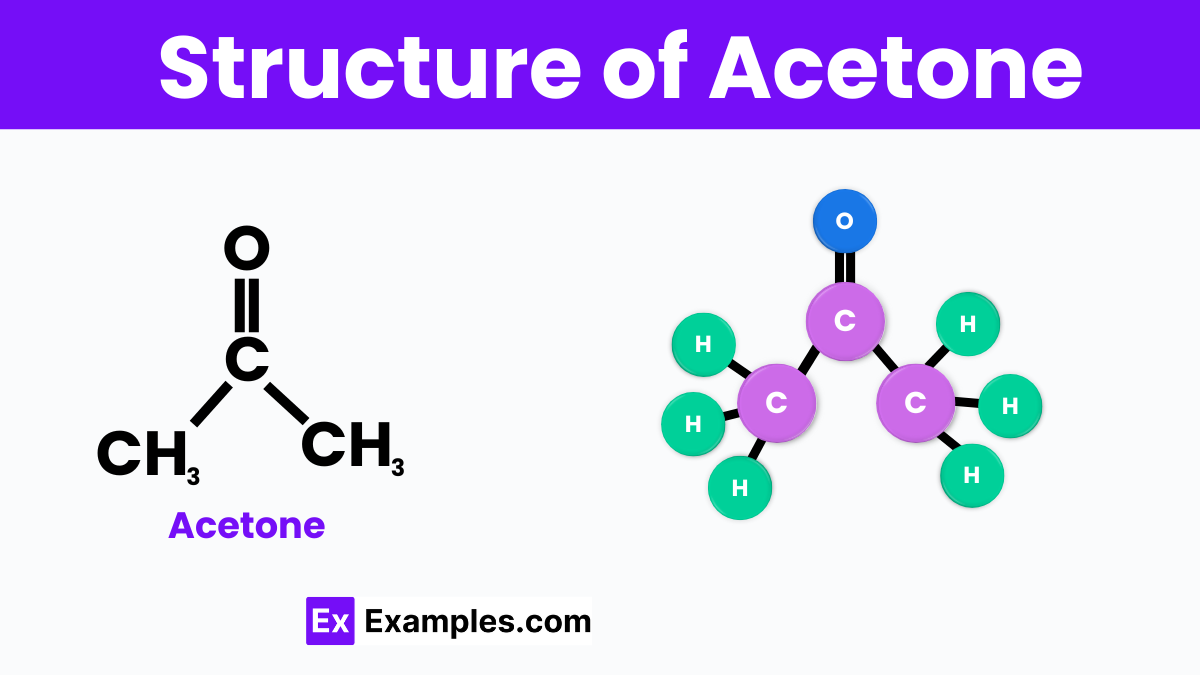
Acetone is also known by its chemical name propanone, has a simple molecular structure consisting of three carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom, represented by the chemical formula C₃H₆O. At the center of the acetone molecule, there is a carbonyl group (C=O), where a carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom. This carbonyl group is flanked on either side by a methyl group (CH₃), making the overall structure symmetrical. The presence of the carbonyl group makes acetone a ketone, which is a type of compound known for its effectiveness as a solvent. This structure is responsible for acetone’s ability to dissolve many organic substances and its quick evaporation rate.
Acetone is commonly produced through the process of cumene oxidation, which is widely used in industrial settings. In this process, cumene (isopropylbenzene) is first oxidized by oxygen from the air to form cumene hydroperoxide. This intermediate compound is then subjected to a process called acid-catalyzed cleavage, where it is broken down into acetone and phenol. The chemical equation representing this reaction is:
(This translates to: Cumene hydroperoxide breaks down into acetone and phenol.)
This method is efficient and produces large quantities of acetone, which is why it is favored for commercial production. The acetone obtained through this process is then purified and used in various applications, ranging from solvents in the nail polish industry to a precursor for other chemical syntheses. This production method showcases the practical application of chemical reactions in industrial chemistry, providing a clear example of how basic organic compounds are transformed into valuable everyday products.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Distinctive, sweetish smell |
| Boiling Point | 56°C (133°F) |
| Melting Point | -95°C (-139°F) |
| Density | 0.79 g/cm³ at 20°C (lighter than water) |
| Solubility | Miscible with water, alcohol, and most organic solvents |
| Vapor Pressure | High (evaporates quickly at room temperature) |
| Flash Point | -20°C (-4°F) (highly flammable) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 67-64-1 |
| Beilstein Number | 635680 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 180 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24850839 |
| SMILES Identifier | CC(=O)C |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C3H6O/c1-3(2)4/h1-2H3 |
| RTECS Number | AL3150000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00008765 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 1 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |

Acetone is perhaps most commonly recognized as the primary component in nail polish remover. Its effectiveness in quickly dissolving nail polish makes it a staple in cosmetic products related to nail care.
Due to its strong solvent properties, acetone is used extensively in the manufacturing and processing of plastics and synthetic fibers. It can dissolve many plastics, making it essential for cleaning and thinning applications in industries.
In scientific research and chemical laboratories, acetone serves as a vital solvent. It is used to clean glassware due to its ability to dissolve organic residues quickly and evaporate without leaving a trace.
Acetone is effective in thinning polyester resin, making it a useful component in the production of fiberglass and a common ingredient in paint thinners for its ability to dissolve and mix with paint.
In the medical field, acetone is used as a skin defatting agent and in various beauty products, aside from its use in nail polish removers. It is also employed to prepare skin for medical procedures.
Acetone acts as an important intermediate in the synthesis of more complex chemical compounds. It is used to produce methyl methacrylate and bisphenol A, crucial precursors to common polymers and plastics.
When it comes into contact with the skin or eyes, this can lead to redness, pain, and in severe cases, chemical burns.
Inhaling acetone vapors, especially in poorly ventilated areas, can irritate the respiratory tract, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, respiratory distress.
Exposure to high concentrations of acetone can cause headaches, dizziness, and a feeling of lightheadedness, which are symptoms of central nervous system depression.
Prolonged inhalation of acetone vapors can lead to nausea and vomiting, as the body reacts to the chemical irritant.
Frequent contact with acetone can remove oils from the skin, leading to dryness, cracking, and dermatitis.
Acetone is highly flammable, posing a significant fire risk if used or stored improperly near open flames or high heat sources.
Not all nail polish removers are 100% acetone; many contain additional ingredients like oils and fragrances.
Acetone is not rubbing alcohol; rubbing alcohol is primarily composed of isopropyl or ethyl alcohol.
Acetone is a ketone, similar to other solvents like MEK (methyl ethyl ketone), but with distinct properties.
Ethyl acetate or rubbing alcohol can be used as alternatives to acetone for many applications.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the molecular formula of acetone?
C₂H₄O
C₃H₆O
C₃H₈O
C₄H₈O₂
Acetone is classified as which type of organic compound?
Alcohol
Aldehyde
Ketone
Ether
What is the IUPAC name for acetone?
Propanal
Propanone
Butanone
Acetaldehyde
Which of the following best describes the odor of acetone?
Sweet
Fruity
Pungent
Odorless
Acetone is miscible with which of the following?
Water
Oil
Hexane
Benzene
What is the primary industrial use of acetone?
As a fuel
As a solvent
As a pesticide
As a food additive
What is the boiling point of acetone?
56°C
78°C
100°C
112°C
In which process is acetone produced as a by-product?
Fermentation
Photosynthesis
Thermal cracking
Dehydration of alcohol
Which enzyme is involved in the metabolism of acetone in the human body?
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Acetone oxidase
Catalase
Cytochrome P450
What type of hazard is associated with acetone?
Corrosive
Flammable
Radioactive
Explosive
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

