What is the square root of 4?
1
2
3
4

The square roots of integers from 1 to 25 highlight a blend of rational and irrational numbers in mathematics, as rational square roots like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 contrast with the irrational roots of the others. Algebraically, understanding squares and square roots helps unravel equations involving these numbers. The integers involved in square roots lay the foundation for deeper exploration in statistics and the least squares method, a technique used to minimize differences between observed and predicted data points. The interplay between rationality and irrationality showcases the elegance and complexity of numerical properties in mathematics.
Download square root 1 to 25 in PDF
The square roots of numbers between 1 and 25 illustrate both rational and irrational values, revealing distinct mathematical properties. In algebra, these roots aid in solving equations and understanding numerical relationships. They also underpin statistical methods like least squares, emphasizing the contrast between different numerical properties.
In exponential form: (x)¹/²
Where x is any number between 1 to 25.
Download square root 1 to 25 in PDF
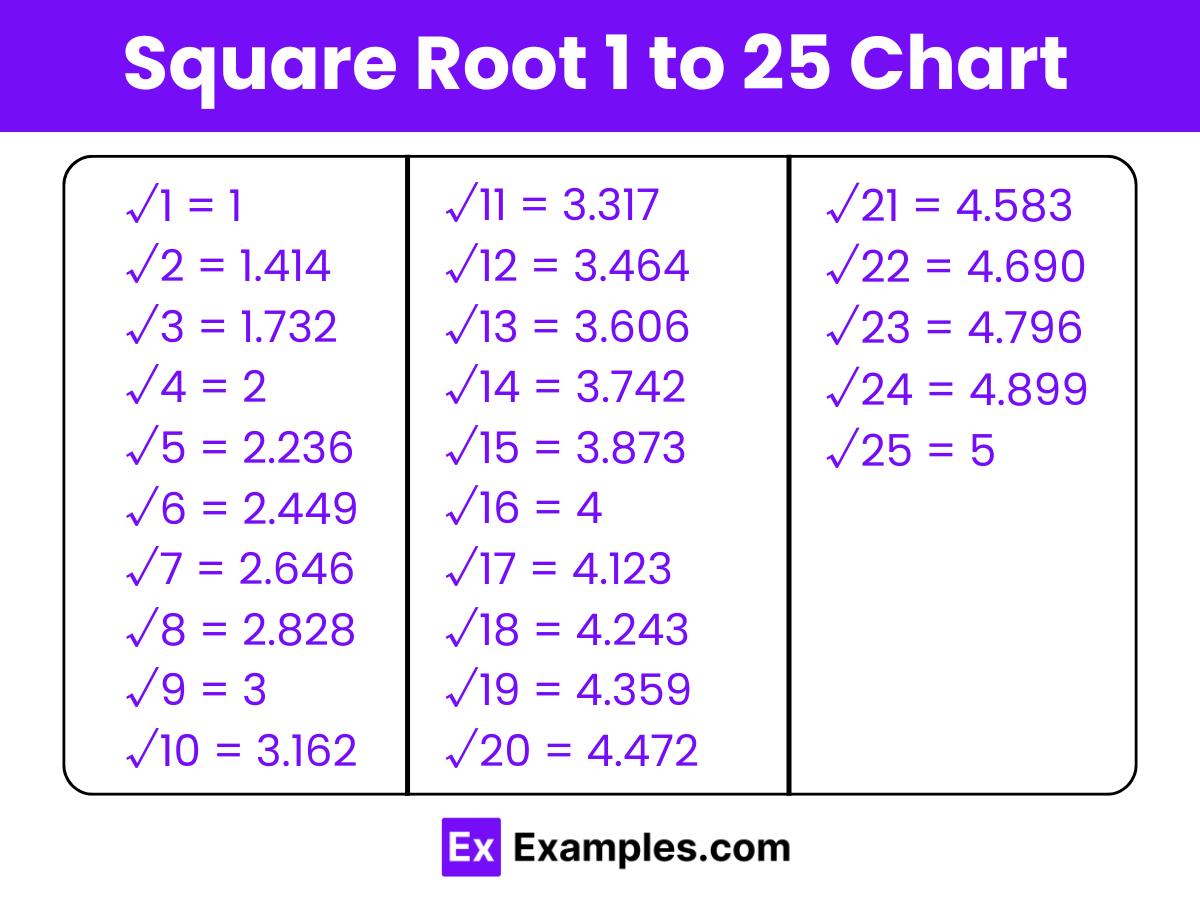
| Square Root from 1 to 25 | |
| √1 = 1 | √14 = 3.742 |
| √2 = 1.414 | √15 = 3.873 |
| √3 = 1.732 | √16 = 4 |
| √4 = 2 | √17 = 4.123 |
| √5 = 2.236 | √18 = 4.243 |
| √6 = 2.449 | √19 = 4.359 |
| √7 = 2.646 | √20 = 4.472 |
| √8 = 2.828 | √21 = 4.583 |
| √9 = 3 | √22 = 4.690 |
| √10 = 3.162 | √23 = 4.796 |
| √11 = 3.317 | √24 = 4.899 |
| √12 = 3.464 | √25 = 5 |
| √13 = 3.606 | |
The square roots of numbers from 1 to 25 reveal a mix of exact integers and non-repeating decimals, showing a combination of rational (like √1, √4, √9) and irrational numbers (like √2, √3, √5). This reflects the diverse numerical properties encountered in mathematics.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| √1 | 1 |
| √4 | 2 |
| √9 | 3 |
| √16 | 4 |
| √25 | 5 |
This table lists the perfect square numbers from 1 to 25 alongside their respective square roots. Perfect squares are numbers that result from multiplying an integer by itself, thus their square roots are integers.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| √2 | 1.414 |
| √3 | 1.732 |
| √5 | 2.236 |
| √6 | 2.449 |
| √7 | 2.646 |
| √8 | 2.828 |
| √10 | 3.162 |
| √11 | 3.317 |
| √12 | 3.464 |
| √13 | 3.606 |
| √14 | 3.742 |
| √15 | 3.873 |
| √17 | 4.123 |
| √18 | 4.243 |
| √19 | 4.359 |
| √20 | 4.472 |
| √21 | 4.583 |
| √22 | 4.69 |
| √23 | 4.796 |
| √24 | 4.899 |
This table provides the square roots of non-perfect squares from 1 to 25. Each entry shows a number and its corresponding square root value.
To calculate the square root of numbers from 1 to 25, you can use several methods:
The numbers with rational square roots from 1 to 25 are 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25. Their square roots are 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
Square roots of non-perfect squares (like 2, 3, 5, etc.) from 1 to 25 are irrational because they cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers, resulting in non-repeating, non-terminating decimals.
In the least squares method, square roots are used to compute the standard deviation and other statistics. The method minimizes the sum of the squares of residuals, which are the differences between observed and predicted values.
While negative square roots don’t exist among real numbers, imaginary numbers like ‘i’ (where i² = -1) allow for the definition of square roots of negative numbers.
Memorizing perfect squares (1, 4, 9, 16, and 25) can be helpful. For others, understanding their approximate square root values and practicing with numerical approximation methods can enhance recall.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square root of 4?
1
2
3
4
Calculate the square root of 9.
2
3
4
5
Find the square root of 16.
3
4
5
6
How much is the square root of 25?
4
5
6
7
Determine the square root of 1.
1
4
2
3
Estimate the square root of 1.
0.5
1
1.5
2
Identify the pattern and calculate the square root of 100.
8
9
10
11
Which is larger, the square root of 25 or 4?
Square root of 25
4
Both are equal
Cannot be determined
If you increase the square root of 16 by one, what do you get?
4
5
6
7
What is the square root of 4, doubled?
2
4
6
8
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

