Making a Lesson Plan with Examples
School is boring. We all know that. But you know what is even more boring? Learning. Everyone detests this in their own little big way. We are forced to go to school and learn stuff that we are not willing to absorb into our little heads. Come on, it is not like we are going to remember all this stuff anyway.
How is quantum physics going to help me deal with my financial debt anyway? Or how is learning the Periodic Table of Elements going to solve world hunger or poverty? They say that education is a right, and not a privilege. But in this modern-day age and society, it is becoming more of a privilege than a right as not everyone is able to actually afford education in the school or university that they desire. There are just some things that we have to choose to retain in our heads while there are some things that we just have to forget about.
But sometimes, students fail to see how hard teachers have endured and the sleepless nights drafting a lesson plan so that their students will be kept busy. It is not the job of the teacher to keep the students entertained or amused during class hours, but to let them learn something so that their parents’ money may actually be put to good use. We have to understand that making lesson plans is harder than it looks, even with the convenience of lesson plan templates that guide the structure and flow. Listed below is the basic structure on how these lesson plans are drafted each and every day.
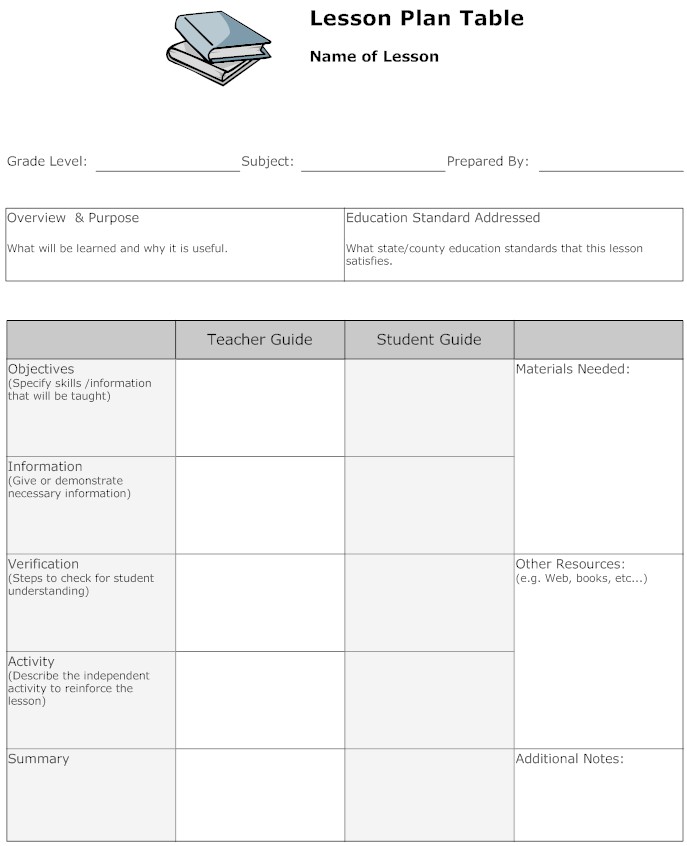
Blank Lesson Plan Example
Creating the Basic Structure
1. Know your objective
There may be a different lesson every day or maybe a 2-part lesson which may take at least two to three days to fully discuss it since it might be too lengthy to finish in one class session. But it is important that each day must have some sort of learning goals for your students. It does not have to be too complicated. It can be as simple as “Learning how to solve quadratic equations using Formula A.” or “Understanding the different communication theories and how they are applied in today’s media society.” You may also see risk plan examples & samples.
2. Write your overview
Some lessons may take days to cover the full scope of the picture. So it is better to provide an overview of the lesson that you might be discussing so that the students may be able to keep track on the different parts of the lesson. For instance, if your coverage is about the novel Les Miserables, a sample overview would not only be the summary of the book, but also the theme that it represents and how it applies in today’s society. You may also like advertising plan examples & samples.
3. Plan your timeline
Planning is essential and critical. If you are that kind of systematic person, you would organize your day and plan out your day in this manner:
- 1:00-1:15: Discussion. Students will be learning how psychology is important in the lives of everyday people with their everyday problems.
- 1:15-1:30: Activity. Students will be paired in groups of 3 and act out a role play on the effects of psychology towards students.
- 1:30-1:40: Surprise exam and checking. Students will be given a 20-item quiz on the lesson that was discussed so far.
- 1:40-1:55: Open forum. Students will be given the chance to ask questions about the lesson for clarification purposes. They may also ask anything that pertains towards the subject itself.
- 1:55-2:00: Conclusion. Students will be asked to read certain lessons in advance to help them prepare for tomorrow’s discussion the next day. An assignment covering the next lesson will also be given. You may also check out annual plan examples and samples.
4. Get to know your students
Developing a teacher-student relationship is perhaps one of the greatest things a teacher can have. It is important to know that every student is born different. Every student is born with different skills, different talents, and yes, different learning abilities. How can a student learn if you are teaching him or her the same kind of learning style that you have been teaching over the past years?
Some students are visual learners, some students are fast learners, some are slow, and some of them are in-between. And in doing so, it is essential hat you at least try to mix up a variety of learning styles to try and cater to the needs of every student in your classroom. You’re bound to have some students that can’t sit through a 25-minute video and others who can’t be bothered to read a two-page excerpt from a book. If you’ve spent a great while talking, stop and let them talk about it. If they’ve been reading, come up with a hands-on activity to put their knowledge to use. You might be interested in risk management examples & samples.
5. Use multiple student interaction patterns
It is called a class for a reason. If it were one-on-one with an instructor or your adviser, then it would not be a classroom discussion anymore. There are students that manage to do well on their own, while there are some who tend to well in group work. Whatever the case is, allow interaction among the students as to allow them to learn in a different way that they might also learn the values of teamwork and coordination between their partners or groupmates. You may also see management plan examples.
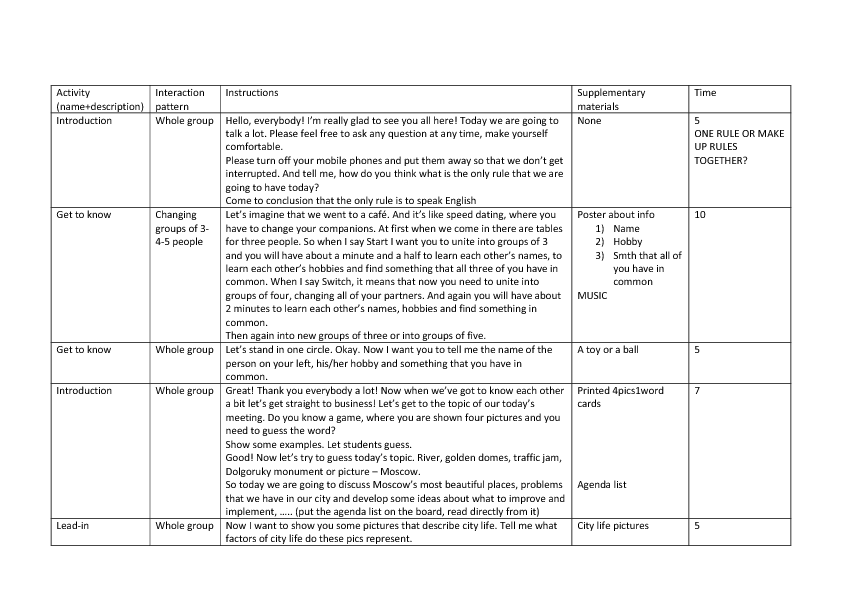
Detailed Lesson Plan Example
Planning Out the Stages
1. Warm them up
Class would normally begin at around 7:30 am in the morning. Sometimes, the day has not even begun and you are already feeling very sleepy. So, what do you do to make sure that you have your students’ full and undivided attention? Warm them up! There are many ways to do so actually: play a game, solve a little brain teaser, do jumping jacks (yes, some teachers do that) or do a little activity that might eventually be connected to the lesson. Anything that can help get them going. You may also see event plan examples & samples.
2. Present the information
Now that you have warmed them up, it’s time to get down to business. It’s time to begin your lesson proper. And there are many ways to go about it. Conventional and old-school teachers would normally grab their chalk or whiteboard marker and proceed to write down the lesson in the blackboard or whiteboard. For modern-day teachers, they would utilize the technology that mankind has provided to society and project their lessons on the screen and from there, they discuss it. But for teachers who are born cool and awesome won’t need the blackboard or projector to discuss their lesson since his or her teaching style is so great that the students will know how to take notes on their own and expose the students to a kind of learning beyond the four corners of the classroom. What comprises is a great teacher is the willingness of the students to keep learning from him or her, not how funny his jokes are. You may also like sales plan examples.
3. Do a guided practice and assess their progress afterwards.
After you have discussed the lesson, how can you determine that the student has learned anything at all from you today? Simple. Give them an activity or an exam that will assess their abilities not only their understanding of the lesson, but also how fast or how slow they actually learn so that you may be able to assist them in the parts that they do not understand, for the lesson proper. The results from that activity would show how much a student is able to understand what you’ve presented to them so far. You may also see transition plan examples & samples.
Once majority of the students are able to comprehend the lesson proper, then you can feel free to move on without worrying too much. If not, then it is best to go back to the lesson and ask them on which parts of the lesson do they not understand properly and ask yourself if you need to present the lesson differently for them to able to understand better. But keep in mind that you cannot afford to be stuck in a lesson for too long, otherwise, the rest of the class would be behind. But it takes two to make it work. The student also has to do everything in his or her power to make sure he or she fully understands the lesson. You may also check out how to create an executive summary of a marketing plan.
4. Leave time for questions
Questions? Violent reactions? Comments? Suggestions? Opinions? By opening the floor to questions, you allow an exchange of ideas and queries that the students are sometimes too afraid to ask the teacher during the lesson proper. By answering these questions from the students, there is a possibility that they might be interested in continuing to learn the lesson further. You might be interested in job plan examples & samples.
5. Conclude the lesson concretely
Once you start discussing, make sure to conclude your lesson properly as well. They say that teaching a lesson is like a conversation between the students. So make sure that you properly end the conversation as well. It would help if you gave the students a bit of a review before leaving the classroom. You may also see personal plan examples & samples.
Lesson Plan Table Example
Just remember that even though you have perfectly concocted out your lesson plan, but it would all be pointless if the students have learned nothing. You may also see audit plan examples & samples.